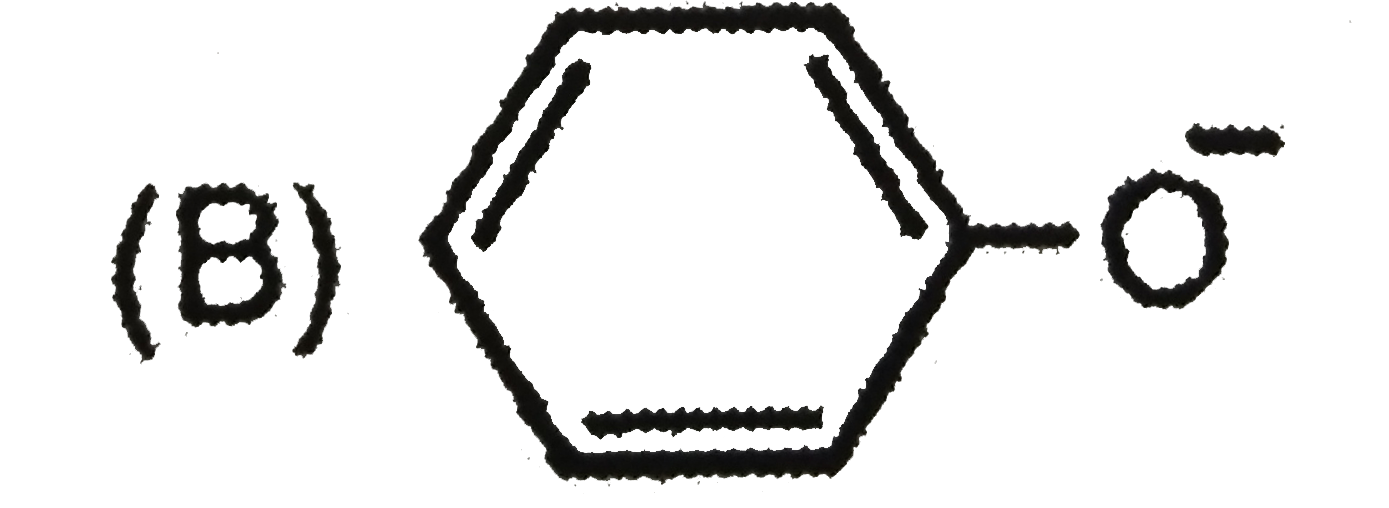
A
B
C
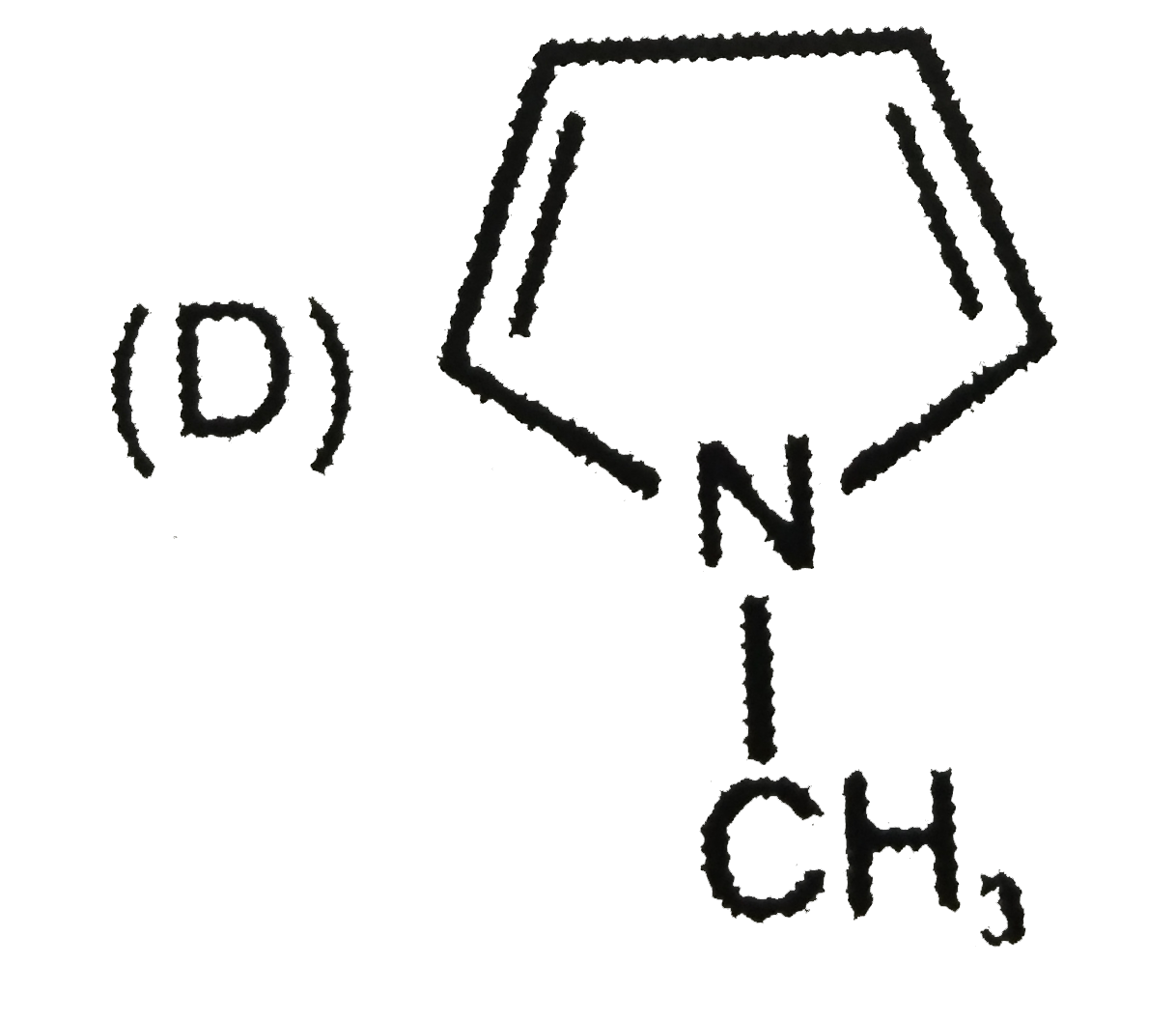
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise EXERCISE-1 PART-III (MATCH THE COLUMN)|1 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise EXERCISE-2 PART-I|20 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART-III : PRACTICE TEST-19|1 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part-III: Section-5: Matching List Type|1 VideosHYDROGEN AND ITS COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise INORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Hydrogen & its compunds Y environment chemistry)|33 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I-EXERCISE-1 PART-II
- Resonance is not possible in
Text Solution
|
- Which does not have conjugate system?
Text Solution
|
- The compound which is not resonance stabilised
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following pairs represents resonating structures ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following pairs represents resonating structures ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following pairs represents resonating structures ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following pairs represents resonating structures ?
Text Solution
|
- Resonance is not possible in
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is least stable ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following resonating structure is the least contributing ...
Text Solution
|
- HNCO (isocyanic acid) has following resonating structures : underset...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the following resonating structures in order of increasing sta...
Text Solution
|
- The most stable resonating structure is
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following groups exerts +m effect when attached with benz...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following groups exerts +m effect when attached with benz...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following group show +M and -l effect?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following group shown +mgt - I effect?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following group show -m and -I effect?
Text Solution
|
- +I effect is shown by
Text Solution
|
- Weakest acid is:
Text Solution
|