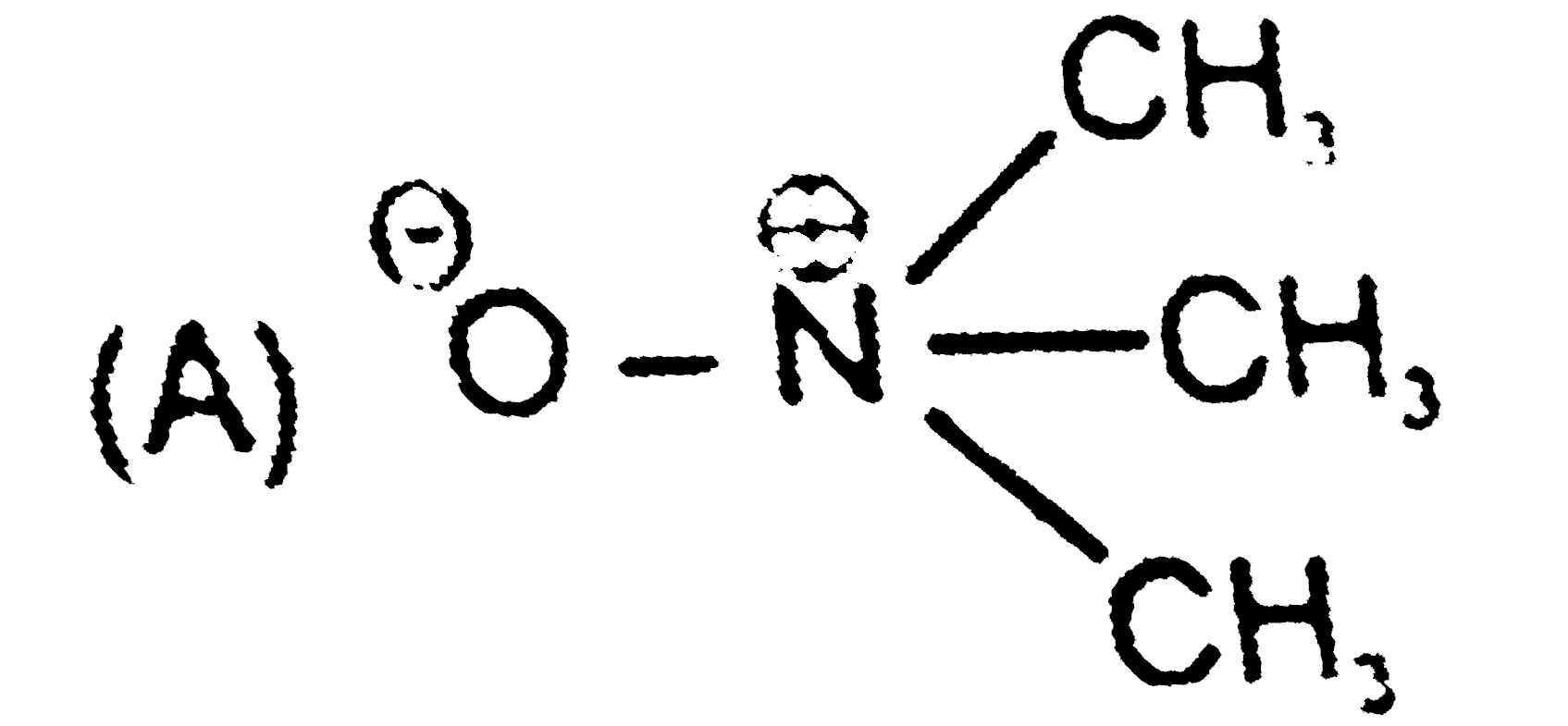
To determine in which cases delocalization of charge is possible, we need to analyze the electronic configurations of the atoms involved and their ability to accommodate charges through resonance or other means. Here’s a step-by-step solution:
### Step 1: Identify the Atoms and Their Charges
- We have different molecules to analyze, specifically focusing on the presence of charges on atoms like nitrogen, phosphorus, and boron.
### Step 2: Analyze Nitrogen (N)
- In the first molecule, there is a positive charge on nitrogen (N).
- The electronic configuration of nitrogen (atomic number 7) is 1s² 2s² 2p³.
- Nitrogen does not have any vacant d orbitals because the d orbitals start from the third energy level (3s, 3p, 3d). Therefore, nitrogen cannot delocalize the positive charge.
**Hint:** Check the electronic configuration of the atom to see if it has vacant d orbitals for charge delocalization.
### Step 3: Analyze Phosphorus (P)
- In the second molecule, we have phosphorus (P) which can have a negative charge.
- The atomic number of phosphorus is 15, and its electronic configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p³.
- Phosphorus has vacant d orbitals (3d), which allows for the delocalization of charge. Therefore, charge delocalization is possible in this case.
**Hint:** Look for the presence of vacant d orbitals in the atom's electronic configuration to determine if delocalization can occur.
### Step 4: Analyze Boron (B)
- In another example, we consider boron (B).
- Boron has an atomic number of 5, with an electronic configuration of 1s² 2s² 2p¹.
- Although boron does not have d orbitals, it has vacant p orbitals that can participate in resonance, allowing for charge delocalization.
**Hint:** Even if d orbitals are not present, check if there are vacant p orbitals that can participate in delocalization.
### Conclusion
Based on the analysis:
- **Delocalization is not possible for nitrogen due to the absence of vacant d orbitals.**
- **Delocalization is possible for phosphorus due to the presence of vacant d orbitals.**
- **Delocalization is also possible for boron due to vacant p orbitals.**
### Final Answer
- Delocalization of charge is possible in the cases of phosphorus and boron (options B, C, and D are correct), while it is not possible in the case of nitrogen (option A is incorrect).