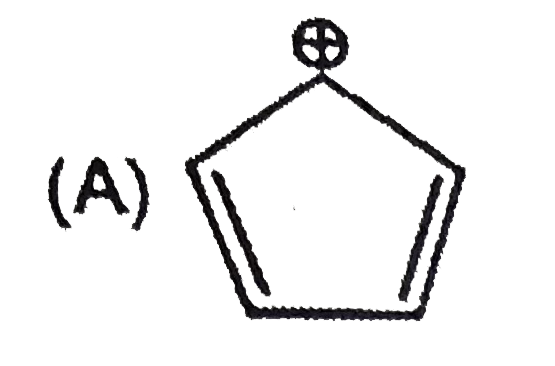
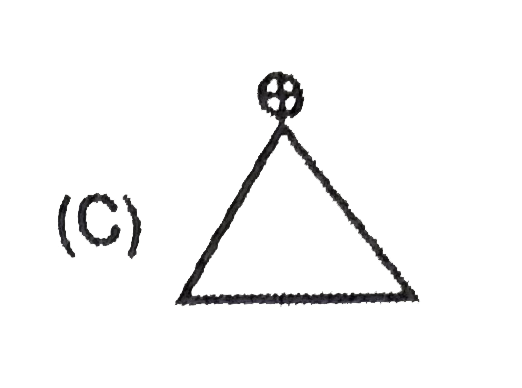
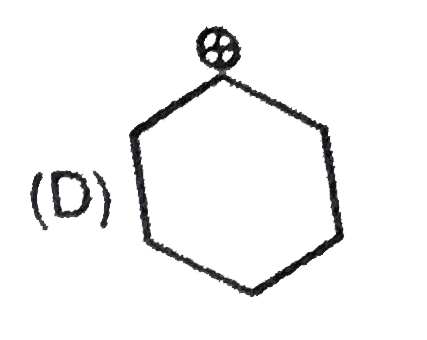
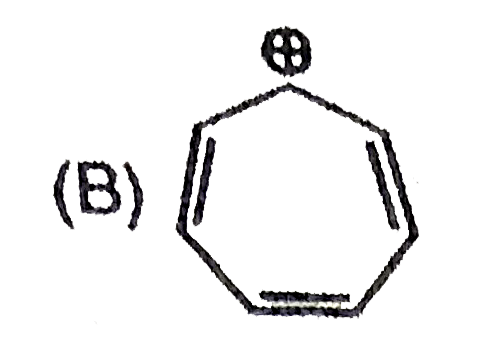A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part-III: Match the Column|2 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part-I : Only One Option Correct Type|22 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-1|20 VideosGASEOUS STATE
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Hydrocarbon)|18 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART-III : PRACTICE TEST-19|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II-Part-II Only One Option Correct Type
- Least stable radical among the following is :
Text Solution
|
- The most stable carbocation is
Text Solution
|
- The most stable carbocation is:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following shows the correct order of decreasing stability...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is the arranged more stable carbocation of the ...
Text Solution
|
- Most stable rearranged form of given carbocations is:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following in the rearranged in the rearranged more stable...
Text Solution
|
- The correct basic strength order of following anions is:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following shows the correct order of decreasing basicity ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the order of basic strength .(If R=Me) ? (I) R(4)N^(+)OH^(-) " ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following cannot be a base?
Text Solution
|
- Select the basic strength order of following molecules ?
Text Solution
|
- Among the following compounds the strongest acid is:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is not correct decreasing k(a) order .
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following acids has the smallest value of dissociation co...
Text Solution
|
- Find the strongest acid among the following compounds is:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following options shows the correct order of decreasing a...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange increasing order of acidic strength of following dibasic acids...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange above phenol in increasing order of pK(a) value:
Text Solution
|
- Order of K(a) of following acids is:
Text Solution
|