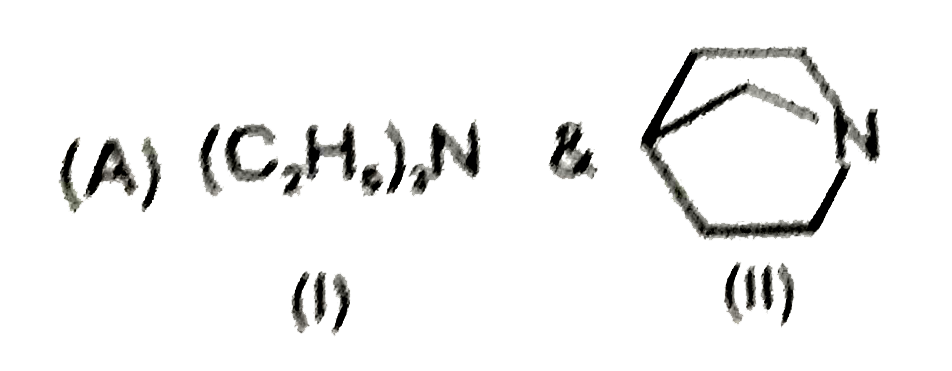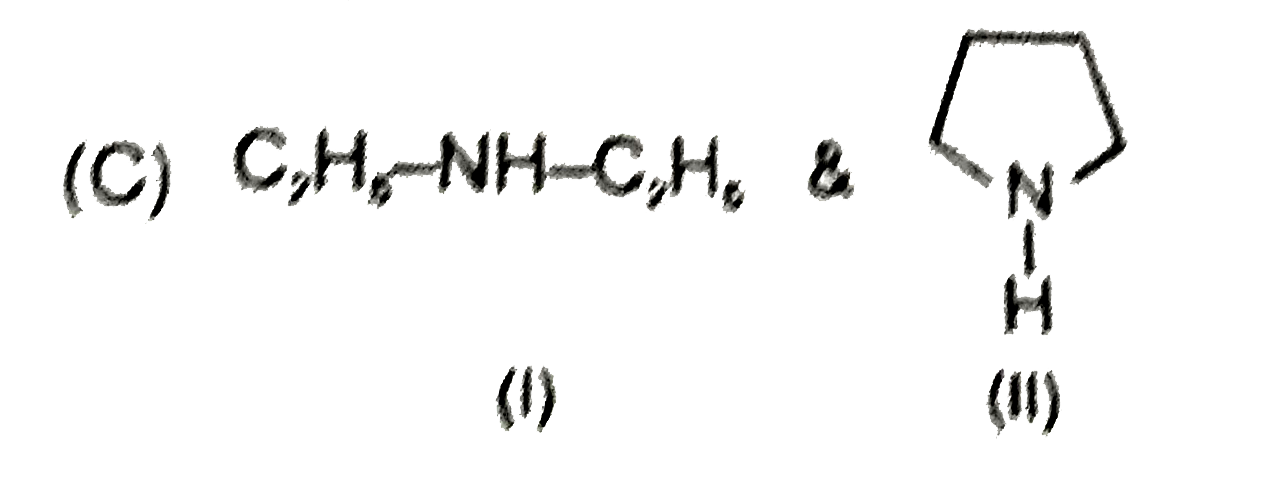A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part-III: Section-4 : Comprehension Type|3 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part-III: Section-5: Matching List Type|1 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part-II: NSEC (Stage-I)|45 VideosGASEOUS STATE
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Hydrocarbon)|18 VideosGENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-I
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART-III : PRACTICE TEST-19|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-GENERAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY II-Part-III: Practice Test-2 (IIT-JEE (Advanced Pattern))
- The decreasing order of stability of following cations is :-
Text Solution
|
- The order of ka values of the following acids is:
Text Solution
|
- The decreasing order of rate of reaction for the following compounds t...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following carbocation is most stable
Text Solution
|
- In which pair the first atom or ion is not larger than the second :-
Text Solution
|
- Which among the following reactions is favoured in forward direction b...
Text Solution
|
- Write the products of the following reactions:
Text Solution
|
- Compare the bond lengths and select the correct option:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds will show tautomerism ?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is correct regarding stability of the following...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are correct statements?
Text Solution
|
- The tautomeric pairs are
Text Solution
|
- In which compounds (II) is more basic than (I)
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following reactions is/are feasible?
Text Solution
|
- In the given molecules the sites undergoes deprotonation and protonati...
Text Solution
|
- In the given molecules the sites undergoes deprotonation and protonati...
Text Solution
|