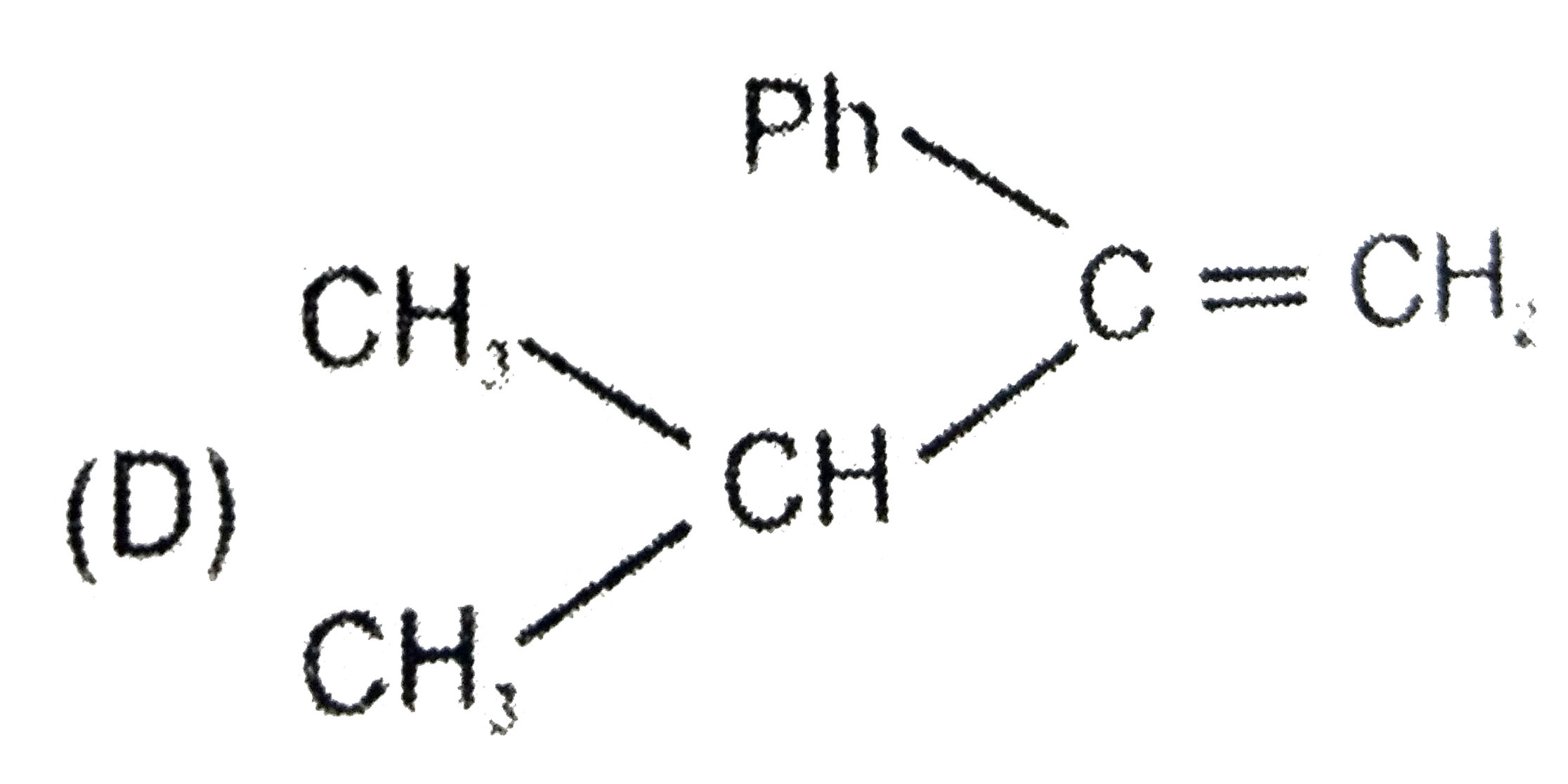
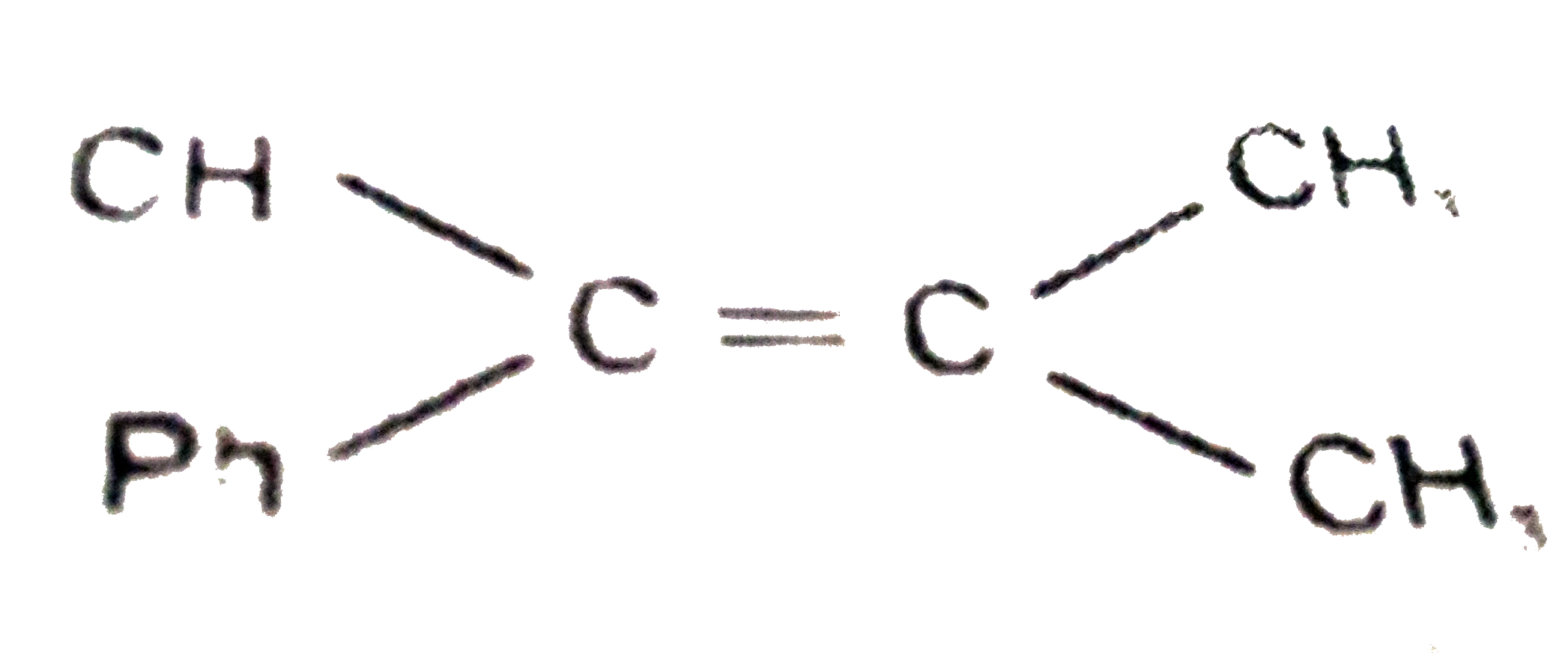A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2 Part-4|5 VideosORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-3 Part-1|20 VideosORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - II
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise-2 Part-2|8 VideosMOLE CONCEPT
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(BASIC CONCEPTS)|27 VideosORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS-IV
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise APSP PART-3|22 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-ORGANIC REACTION MECHANISMS - II-Exercise-2 Part-3
- Electrophilic aromatic substitution can be seen in which of the follow...
Text Solution
|
- In which of the following reactions correct major product has be menti...
Text Solution
|
- Which is the correct relationship mentioned in bracket :
Text Solution
|
- Paedogenesis is observed in
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are correct for above reaction .
Text Solution
|
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds will give same major product on acid ...
Text Solution
|
- True statement about above reaction :
Text Solution
|
- CH(3) -CH =CH(2) + HOBr to P, The major product P is
Text Solution
|
- Identify the incorrect statement
Text Solution
|