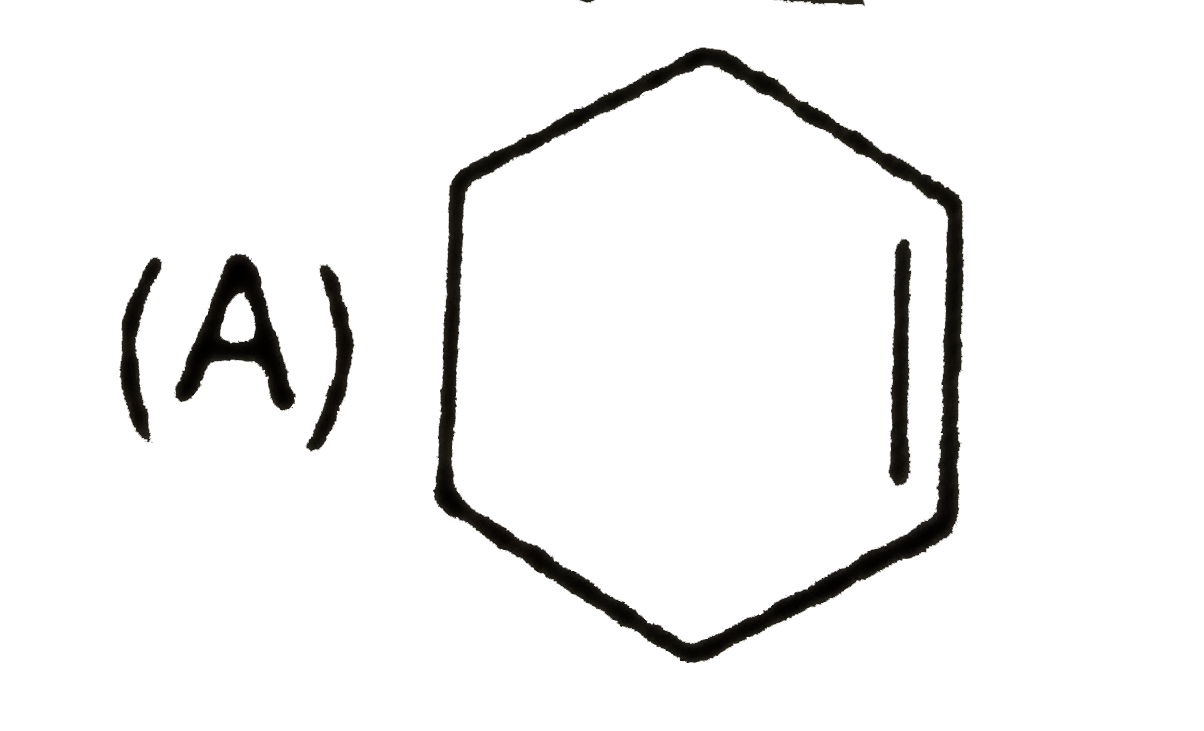
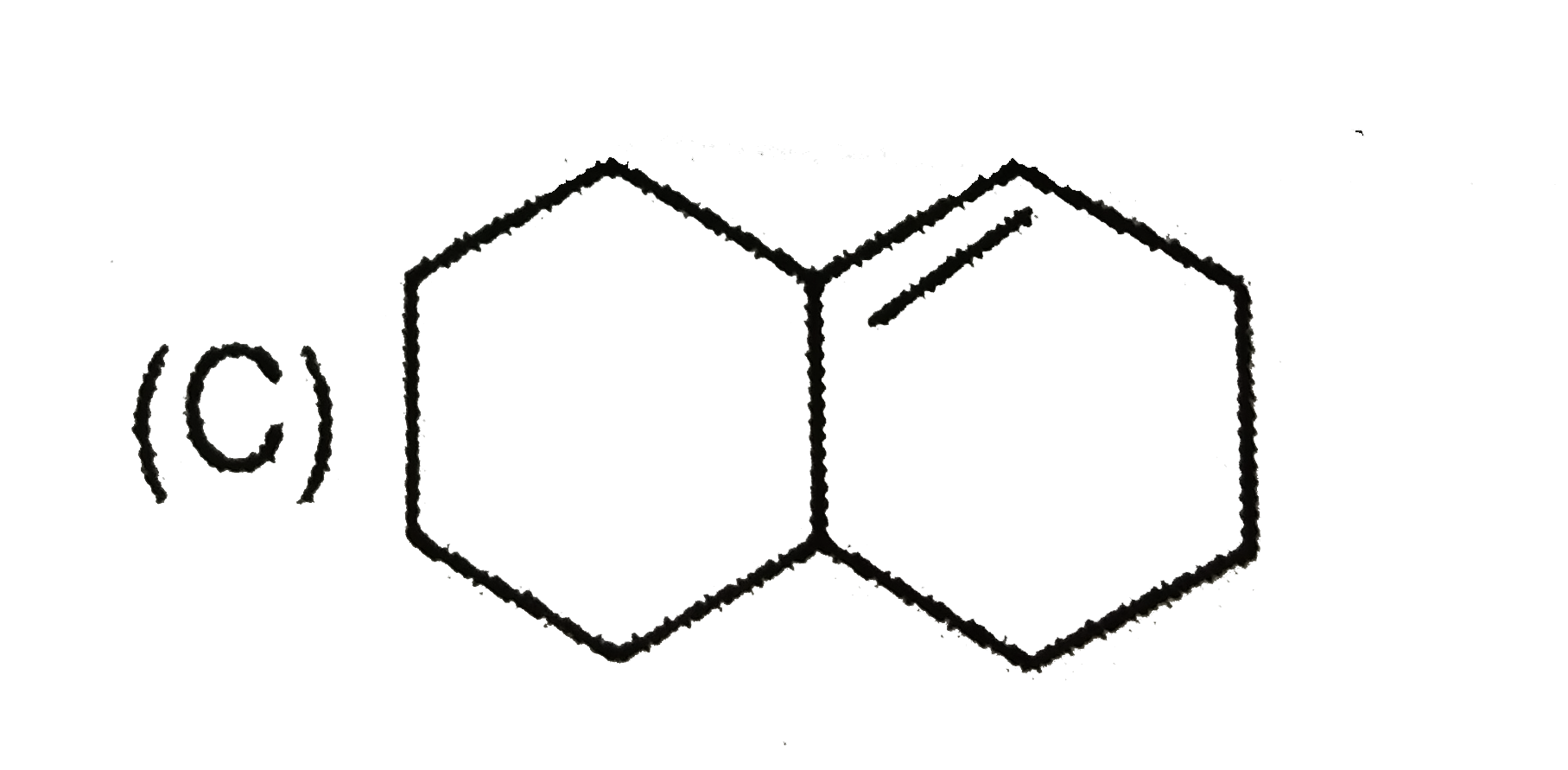
A
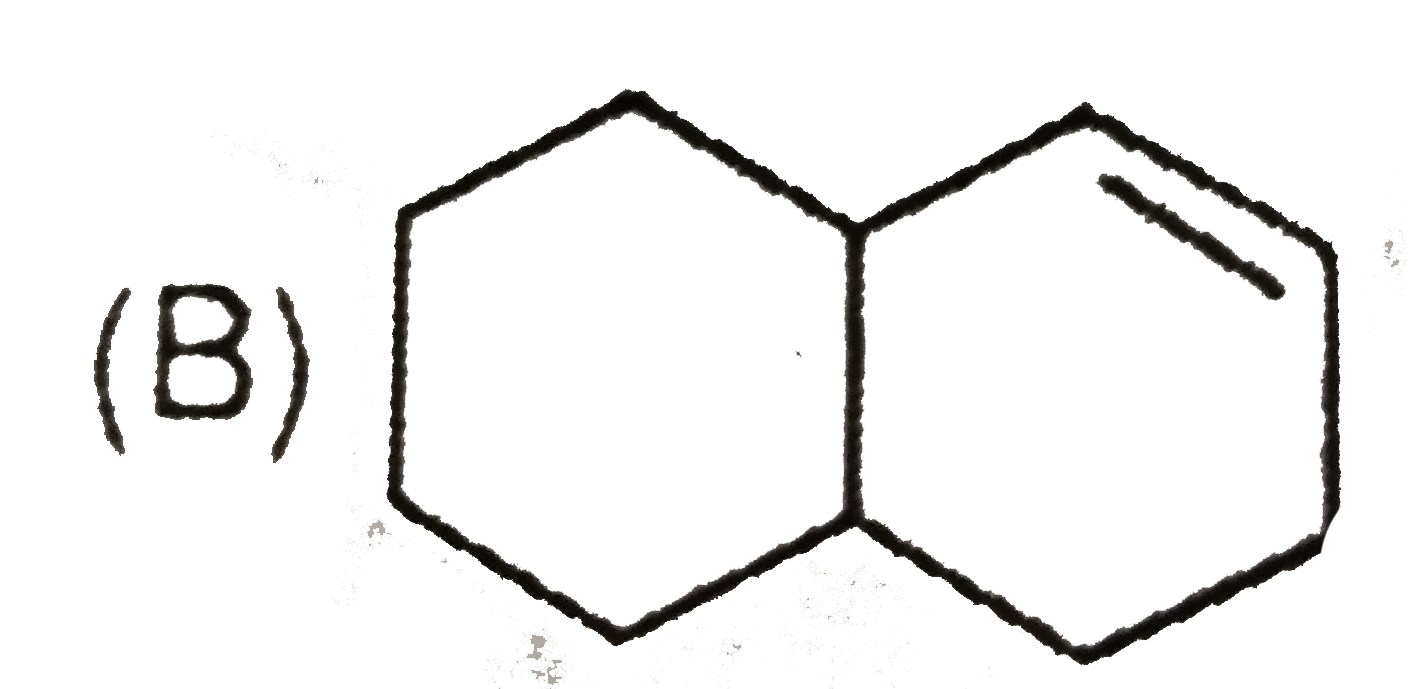
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
STRUCTURAL IDENTIFICATION & PRACTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part-II INTEGER|8 VideosSTRUCTURAL IDENTIFICATION & PRACTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Comprehension|4 VideosSTRUCTURAL IDENTIFICATION & PRACTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part-III Match the column|1 VideosSOLID STATE
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part- IV|21 VideosTHERMODYNAMIC & THERMOCHEMISTRY
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise INORGANIC CHEMISTRY(P-Block Elements)|26 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-STRUCTURAL IDENTIFICATION & PRACTICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-Exercise-2 only one option correct
- How many products (structural isomers only ) are formed by monochlorin...
Text Solution
|
- Compound 'X' is
Text Solution
|
- The chemical reaction of an unsaturated compound 'M' are given below. ...
Text Solution
|
- Red precipitate underset(NH(4)OH)overset(Cu(2)Cl(2))larrP(C(5)H(8))ove...
Text Solution
|
- Compound A(C(3)H(5)N) gives precipitate with Tollen's reagent and H(2)...
Text Solution
|
- Observe the following compound and select +ve & -ve test respectively.
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following amines does not react with Hinsberg's reagent?
Text Solution
|
- Lassaigne's test for the detection of nitrogen will fail in the case ...
Text Solution
|
- The sodium extract of an organic compound on treatment with FeSO(4) s...
Text Solution
|
- A unsaturated hydrocarbons (P) on reductive ozonolysis produce an dica...
Text Solution
|
- An organic compound with 68.9 % of C and 4.92 % of H, is aromatic and...
Text Solution
|