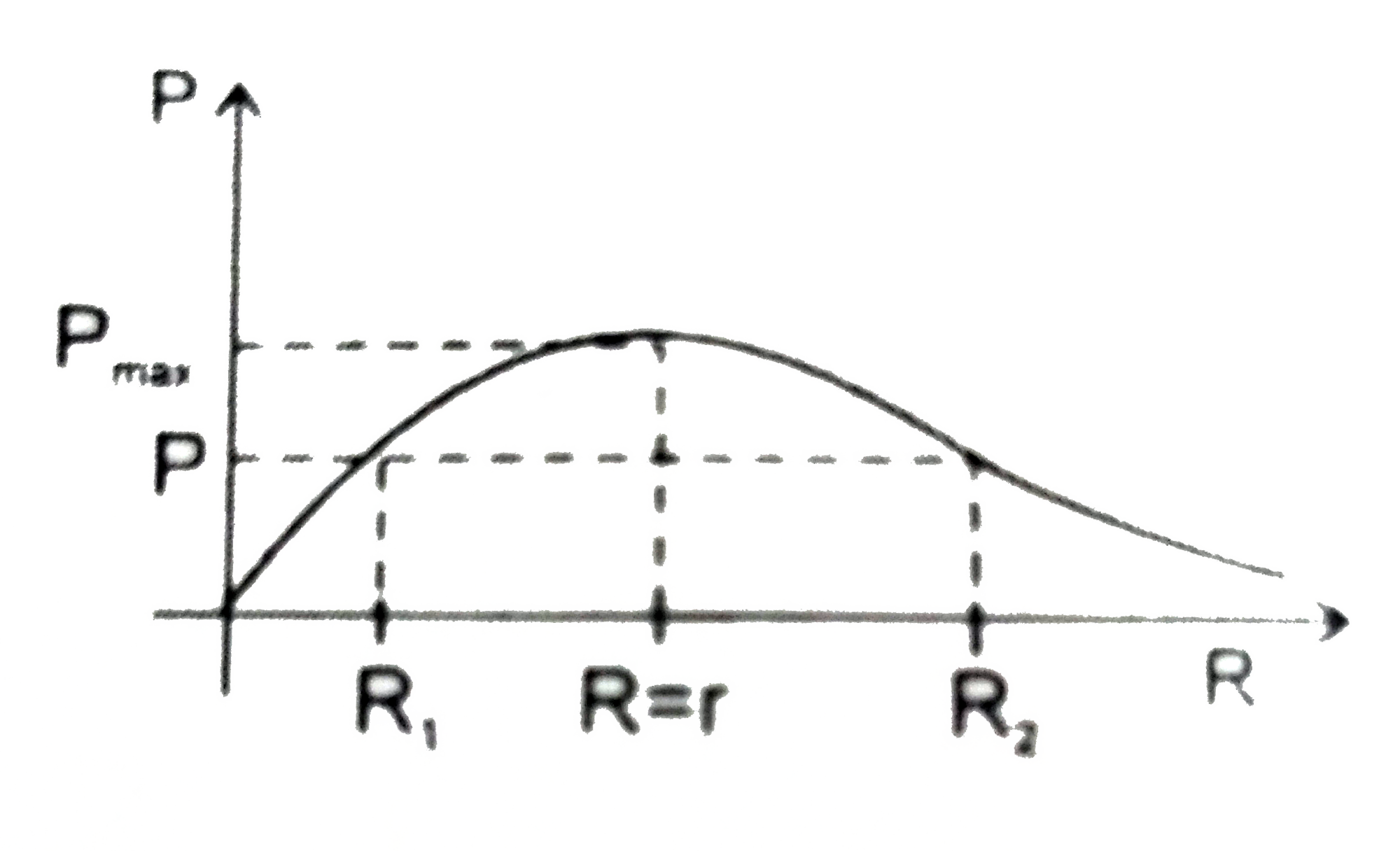
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-CURRENT ELECTRICITY-High Level Problems (HIP)
- A body of mass 10 kg and velocity 10 m/s collides with a stationary bo...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer having 30 divisions has a current sensitivity of 20 mu ...
Text Solution
|
- A 100 V voltmeter of internal resistance 20 kOmega in series with a hi...
Text Solution
|
- A perosn decides to use his bath tub water to generate electric power ...
Text Solution
|
- A cell of emf 3.4 V and internal resistance 3 Omega is connected to an...
Text Solution
|
- When a cell is conneted in a circuit, a current 1(1) flows in the circ...
Text Solution
|
- A battery is made by joining m rows of identical cells in parallel. Ea...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in figure, all wires have equal resistance r. Fin...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer having a coil resistance of 100 Omega gives a full scal...
Text Solution
|
- A 6V battery of negligible internasl resistance is connected across a ...
Text Solution
|
- The emf (epsilon)and the internal resistance r of the battery shown in...
Text Solution
|
- Consider an infinite ladder of network shown In fig 5.223. A voltage i...
Text Solution
|
- Find the resistance R(AB) of the frame made of a thin wire. Assume tha...
Text Solution
|
- A nichrome wire uniform cross-sectional area is bent to form a rectang...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform wire AB of length 1 m, an unknown resistance X, and a r...
Text Solution
|
- A thin wire of length L and cross-sectional area A oriented in the x-d...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer vaving 50 divisions provided with a variable shunt S is...
Text Solution
|
- Standard rating of each bulb is P, V. If total power consumption by co...
Text Solution
|
- If the reading of ammeter A(1)in figure is 2.4 A, what will the ammete...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal cell having a steady emf of 2 volt is connected across the po...
Text Solution
|