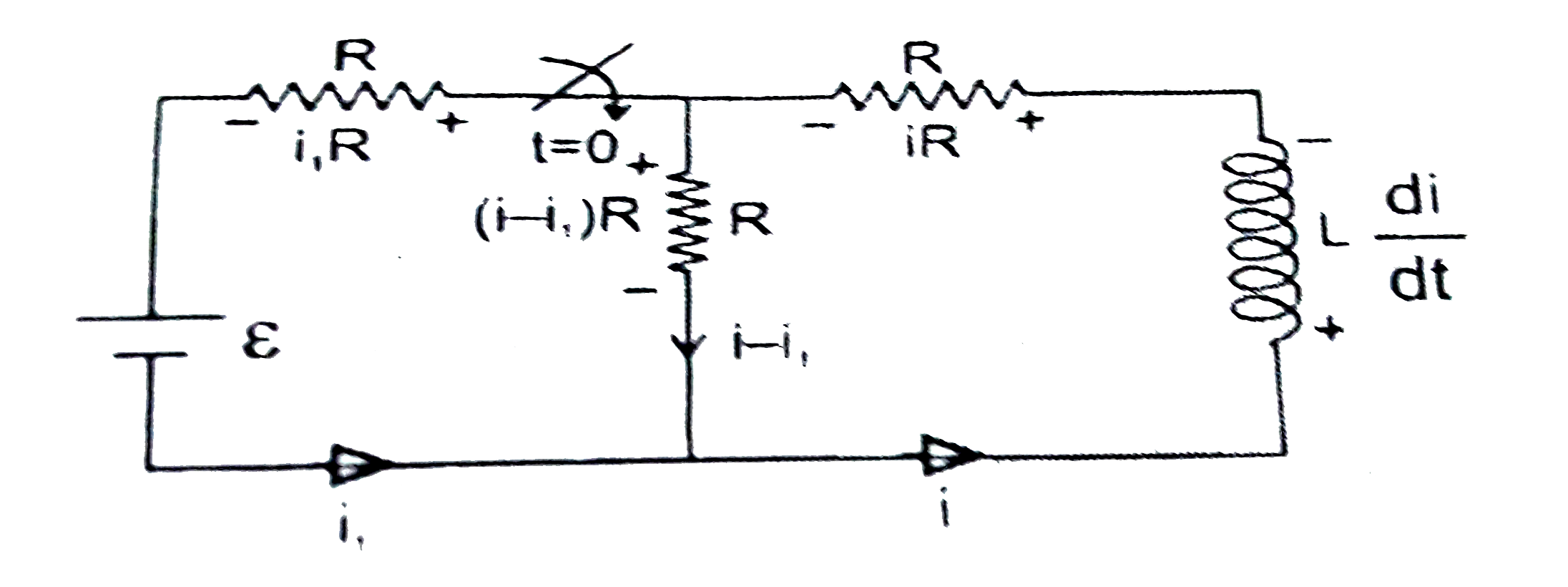
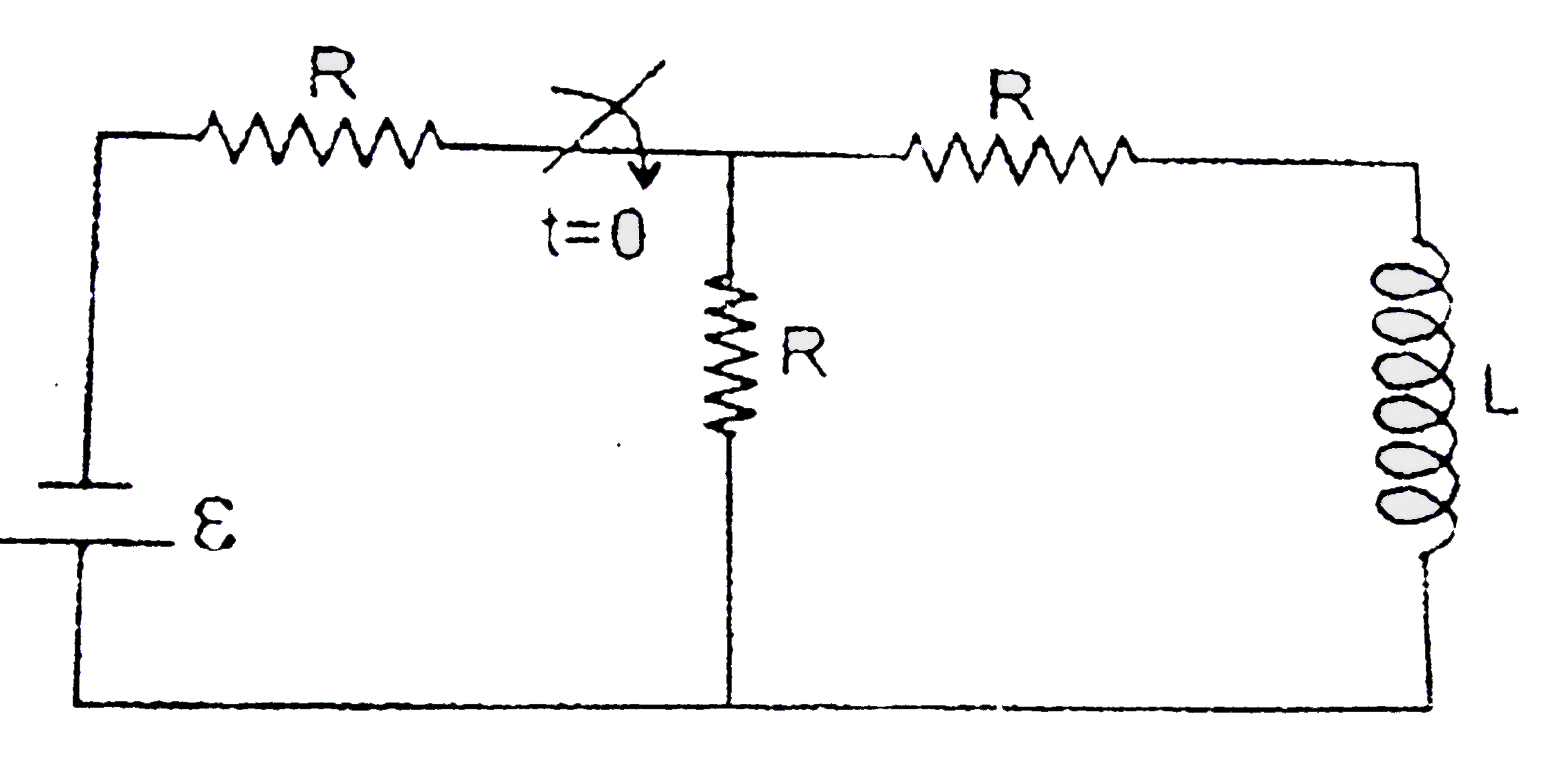Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In the following circuit the switch is closed at t=0.Intially there is...
Text Solution
|
- The switch in figure is closed at time t = 0 . Find the current in the...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, switch S is closed at time t = 0 . Find the curr...
Text Solution
|
- In the following circuit (Fig.)the switch is closed at t = 0. Intially...
Text Solution
|
- A circuit contains an ideal cell and an inductor with a switch. Initia...
Text Solution
|
- there in no current part of this circuit for time t lt o. Switch S is ...
Text Solution
|
- there in no current part of this circuit for time t lt o . Switch S is...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit diagram shown, intially there is no energy in the induc...
Text Solution
|
- At t=0 , switch S is closed. Find time constant of the circuit and cur...
Text Solution
|