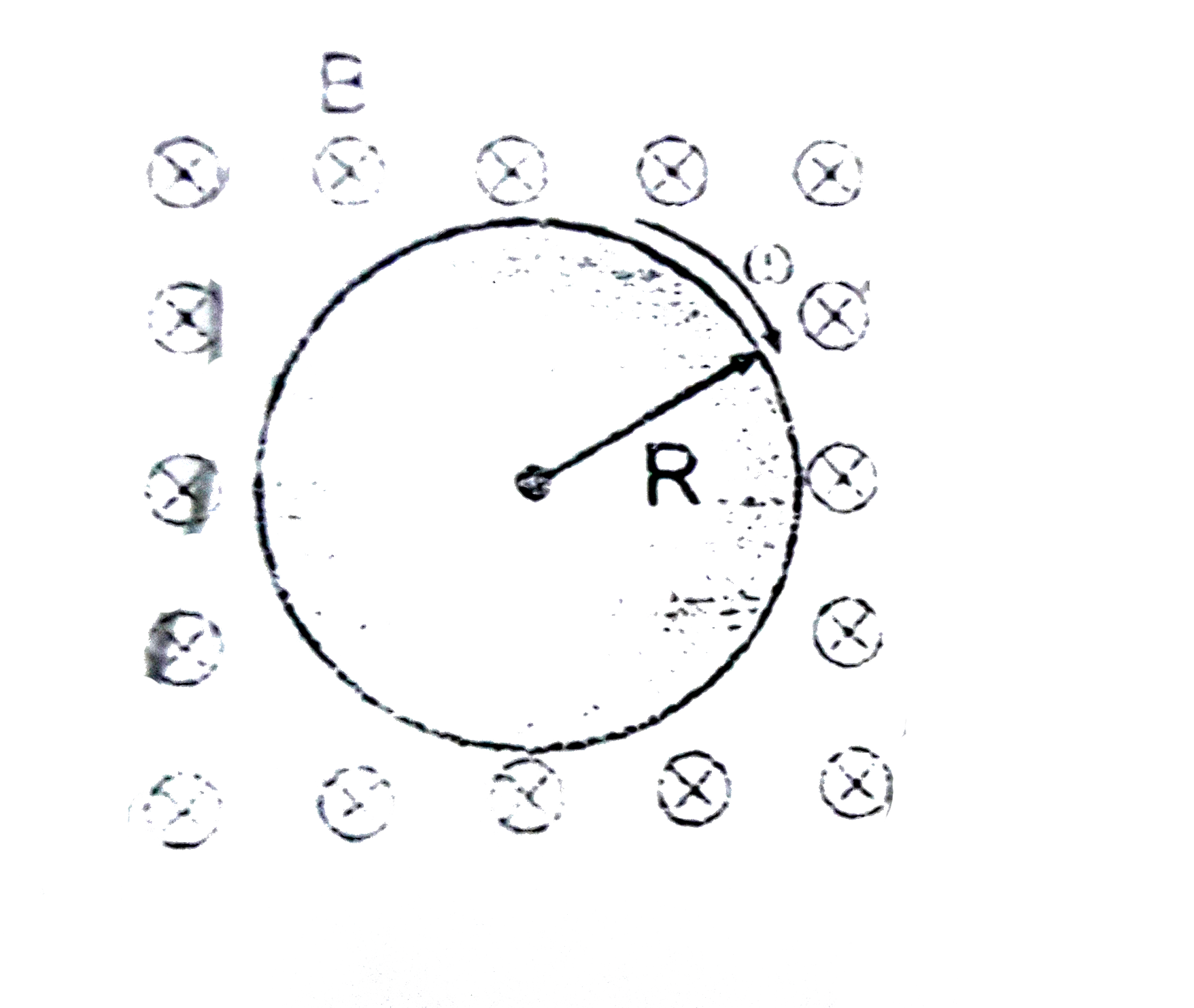A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A conducting disc of radius R is placed in a uniform and constant magn...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting disc of radius r rotates with a small but constant angu...
Text Solution
|
- A charge q is uniformly distributed on a non-conducting disc of radius...
Text Solution
|
- Find the ratio of magnetic dipole moment and magnetic field at the cen...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting thin disc of radius R and mass m having charge unifor...
Text Solution
|
- A thin metallic disc is rotating with constant angular velocity about ...
Text Solution
|
- A flat disc of radius R charged uniformly on its surface at a surface ...
Text Solution
|
- A non-conducting disc having unifrom positive charge Q , is rotating a...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting disc of radius R is placed in a uniform and constant magn...
Text Solution
|