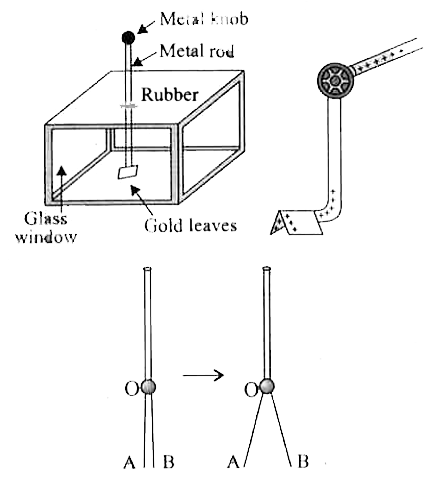
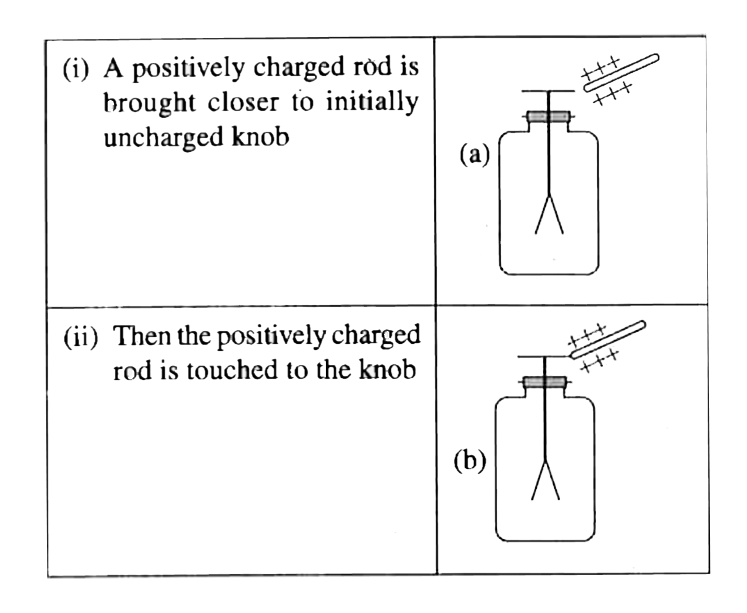
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise - 3 Part - I|33 VideosELECTROSTATICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part - II|23 VideosELECTROSTATICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise Part- II|20 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise A.l.P|19 VideosEXPERIMENTAL PHYSICS
RESONANCE ENGLISH|Exercise PART -II|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-ELECTROSTATICS-Part - IV
- A leaf electroscope is a simple apparatus to detect any charge on a bo...
Text Solution
|
- A leaf electroscope is a simple apparatus to detect any charge on a bo...
Text Solution
|
- A leaf electroscope is a simple apparatus to detect any charge on a bo...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle is suspended at the center of two thin concentric s...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle is suspended at the center of two thin concentric s...
Text Solution
|
- A charged particle is suspended at the center of two thin concentric s...
Text Solution
|
- A solid conducting sphere of radius 'a' is surrounded by a thin unchar...
Text Solution
|
- A solid conducting sphere of radius 'a' is surrounded by a thin unchar...
Text Solution
|
- A solid conducting sphere of radius 'a' is surrounded by a thin unchar...
Text Solution
|