Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE ENGLISH-ELECTROSTATICS-HLP
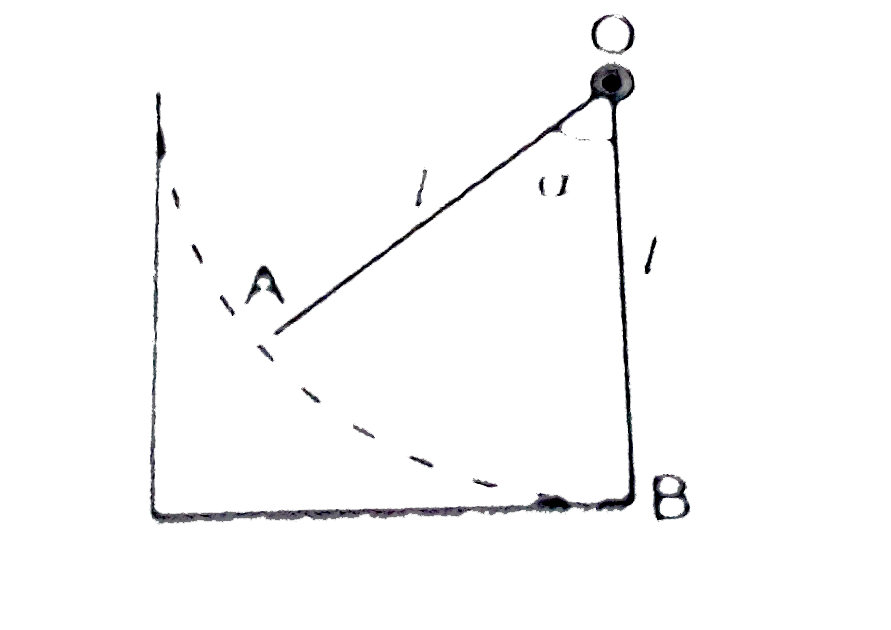
- An electrometer consister of a fixed vertical metal bar OB at the top ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod AB of mass m and length l is hinged at its mid point C. ...
Text Solution
|
- Three equal charge q(0) each are placed at three corners of an equilat...
Text Solution
|
- A solid of radius 'R' is uniformly charged with charge density rho in ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform surface charge of density sigma is given to a quarter of a d...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a rod of length L which is uniformly charged with linear ...
Text Solution
|
- A charged ball of mass 5.88xx10^(-4) kg is suspended from two silk str...
Text Solution
|
- A charge of 16xx10^(-9) C is fixed at the origin of coordinates. A sec...
Text Solution
|
- Two large conducting plates are placed parallel to each other with a ...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 10^(-2) kg and having charge + 3 xx 10^(-6)C is tied at...
Text Solution
|
- A system consists of a thin charged wire ring of radius r and a very l...
Text Solution
|
- A thin nonconducting ring of radius R has a linear charge density ...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges q and -q are separated by a distance 2a. Evaluate th...
Text Solution
|
- A system consits of a uniformly charged sphere of radius R and a surro...
Text Solution
|
- Find the electric field potential and strength at the center of a hem...
Text Solution
|
- A nonconducting disk of radius a and uniform positive surface charge d...
Text Solution
|
- The potential difference between two large parallel plates is varied a...
Text Solution
|
- Four point charges +8muC-1muC,-1muC and +8muC are fixed at the points ...
Text Solution
|
- A small ball of mass 2 xx 10^-3 kg, having a charge 1 mu C, is suspend...
Text Solution
|
- Three point charges q, 2q and 8q are to be placed on a . 9cm long st...
Text Solution
|