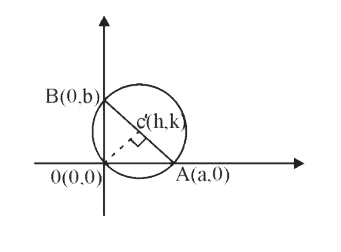
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
JEE MAIN REVISION TEST - 7|JEE - 2020
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Mathematics (Section - 2) Numercial type questions|5 VideosJEE MAIN REVISION TEST - 4 JEE - 2020
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise MATHEMATICS|25 VideosJEE MAIN REVISION TEST -14
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise MATHEMATICS (SECTION 2)|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-JEE MAIN REVISION TEST - 7|JEE - 2020-Mathematics (Section - 2) Numercial type questions
- A circle of constant radius r passes through the origin O, and cuts th...
Text Solution
|
- In a class of 60 students, 40 opted for NCC, 30 opted for NSS and 20 o...
Text Solution
|
- Let S and S' be the foci of the ellipse and B be any one of the extrem...
Text Solution
|
- If sin^(4) alpha + 4 cos^(4) beta + 2 = 4sqrt(2) sin alpha cos beta, a...
Text Solution
|
- The integral int(3x^13+2x^11)/((2x^4+3x^2+1)^4)dx is equal to (where C...
Text Solution
|
- Let f(x)=x^3-3(a-2)x^2+3ax+7 and f(x) is increasing in (0,1] and decre...
Text Solution
|