A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-JEE MAIN REVISION TEST 8 (2020)-CHEMISTRY (SECTION 2)
- Two solids dissociates as follows . The total pressure when both ...
Text Solution
|
- Decomposition of X exhibits a rate constant of 0.5 mu g // year. How ...
Text Solution
|
- what is the work fuction of the metal if the light of wavelength 4...
Text Solution
|
- The standard electrode potential E^(Theta) and its temperature coeffic...
Text Solution
|
- 50 mL of 0.5 M oxalic acid is needed to neutralize 25 mL of sodium hyd...
Text Solution
|
- Iodine reacts with concentrateed HNO3 to yield Y along with other prod...
Text Solution
|
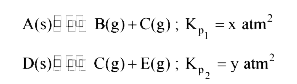 .
. 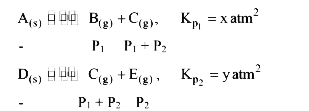 .
.