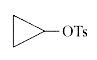
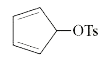
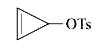
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-JEE MAIN REVISION TEST - 18-CHEMISTRY - SECTION 2
- Among the following, the compound that undergoes the fastest SN1 react...
Text Solution
|
- It has been found that 0.290 g of an organic compound containing C, H ...
Text Solution
|
- The number of elements expected in the g-block of the periodic table i...
Text Solution
|
- In a 3D hexagonal unit cell of identical atoms, the number of atoms th...
Text Solution
|
- H2 (gas) is bubbled through an aqueous solution of HCl(pH = 2.5) at 25...
Text Solution
|
- What is the coordination number of Ce^(+4) in the complex cerric ammo...
Text Solution
|