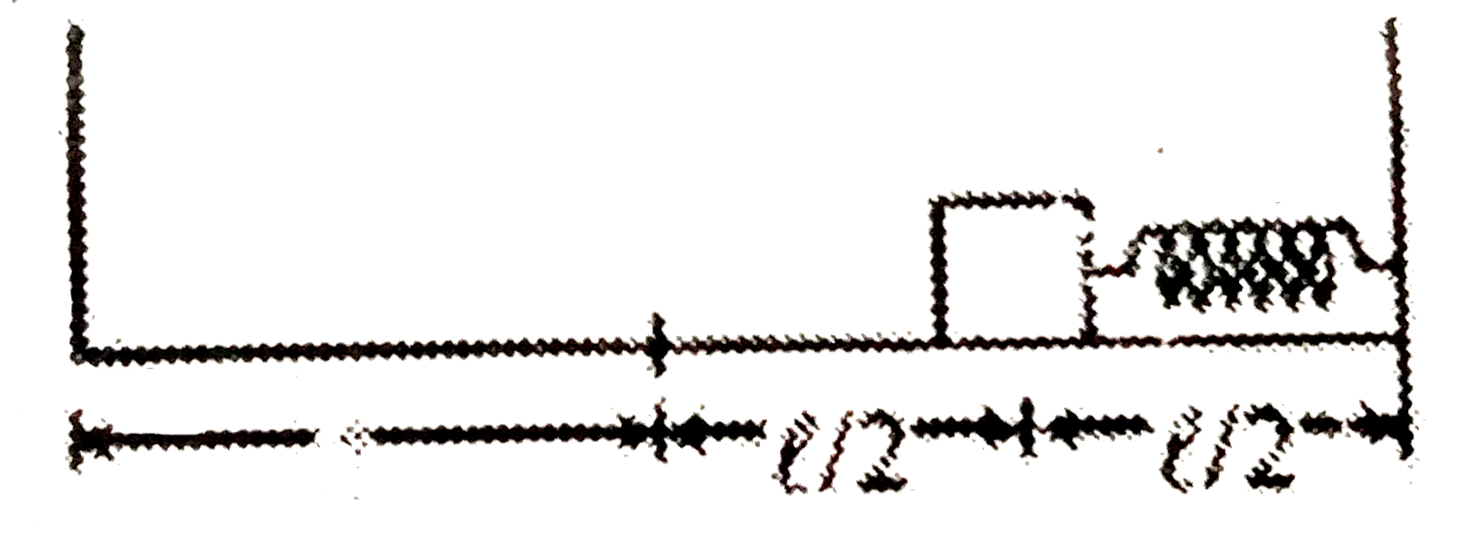A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL (2)|40 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise 6-previous year question|56 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL 0 LONG ANSWER TYPE|2 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive) (True/False Type)|3 VideosSYSTEM OF A PARTICLES & ROTATIONAL MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE F|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION -LEVEL (1)
- A block is kept on a rough horizontal plank. The coefficient of fricti...
Text Solution
|
- A thin bar of mass M and length L is free to rotate about a fixed hori...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m compresses a spring iof stifffness k through a dista...
Text Solution
|
- One end of an ideal spring is fixed to a wall at origin O and axis of ...
Text Solution
|
- One end of an ideal spring is fixed to a wall at origin O and the axis...
Text Solution
|
- One end of an ideal spring is fixed to a wall at origin O and the axis...
Text Solution
|
- Amplitude of a swing decreases to 0.5 times its original magnitude in ...
Text Solution
|
- The amplitude of a simple pendulum, oscillating in air with a small sp...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum with time period of 1s is losing energy due to damping. At ...
Text Solution
|
- The angular frequency of the damped oscillator is given by omega=sqrt(...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 0.10 kg has its velocity varying according to the r...
Text Solution
|
- A plank with a bar placed on it performs horizontal harmonic oscillati...
Text Solution
|
- A tiny mass performs S.H.M along a straight line with a time period of...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity-time diagram of a harmonic oscillator is shown in adjoinn...
Text Solution
|
- A cubical block of mass M vibrates horizontally with amplitude of 4.0 ...
Text Solution
|
- A mass hangs in equilibrium from a spring of constant K=2N//cmAnothe...
Text Solution
|
- The acceleration and velocity maximum of simple harmonically oscillati...
Text Solution
|
- A body of mass 36 g moves with S.H.M. of amplitude A = 13 cm and time ...
Text Solution
|
- The tension along a string at its mean position is 1% more than its we...
Text Solution
|
- The amplitude of a lightly damped oscillator decreases by 4.0% during ...
Text Solution
|