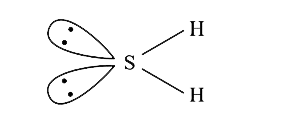
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-CHEMICAL BONDING-I & II-JEE Advanced (Archive)
- The corrrect order of C-O bond length among CO, CO3^(2-), CO2 is
Text Solution
|
- In overset(1)CH(2)=overset(2)CH-overset(3)CH(2)-overset(4)C-=overset(5...
Text Solution
|
- The geometry of H2S and its dipole moment are
Text Solution
|
- Write the molecular orbital electron distribution of oxygen (O(2)) Spe...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the molecular structures of XeF(2), XeF(4) and XeO(2)F(2), indica...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is correct among the species CN^(Θ),C...
Text Solution
|
- Molecular shape of XeF(2), BeF(2) and CF(2) are :
Text Solution
|
- Nodal planes of pi-bonds in CH(2)=C=C=CH(2) are located in,
Text Solution
|
- The hybridization of atomic orbitals of nitrogen in N(3)^(-),(H(3)Si)(...
Text Solution
|
- Specify the coordination geometry around and hybridisation of N and B ...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the least stable ion amongst the following:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following molecular species has unpaired electrons(s) ? .
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following molecules has highest dipole moment?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following are iso-electronic as well as iso-structural ? ...
Text Solution
|
- Using VSEPR theory draw the shape of PCI(5) and BrF(5) ?.
Text Solution
|
- The number of lone piar(s) in XeOF(4) is .
Text Solution
|
- One the basic of ground electronic configuration, arrange the followin...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the shape of XeF(4) and OSF(4) according to VSEPR theory Show the...
Text Solution
|
- According to MO theory .
Text Solution
|
- Predict whether the following molecules are isostructural or not Justi...
Text Solution
|