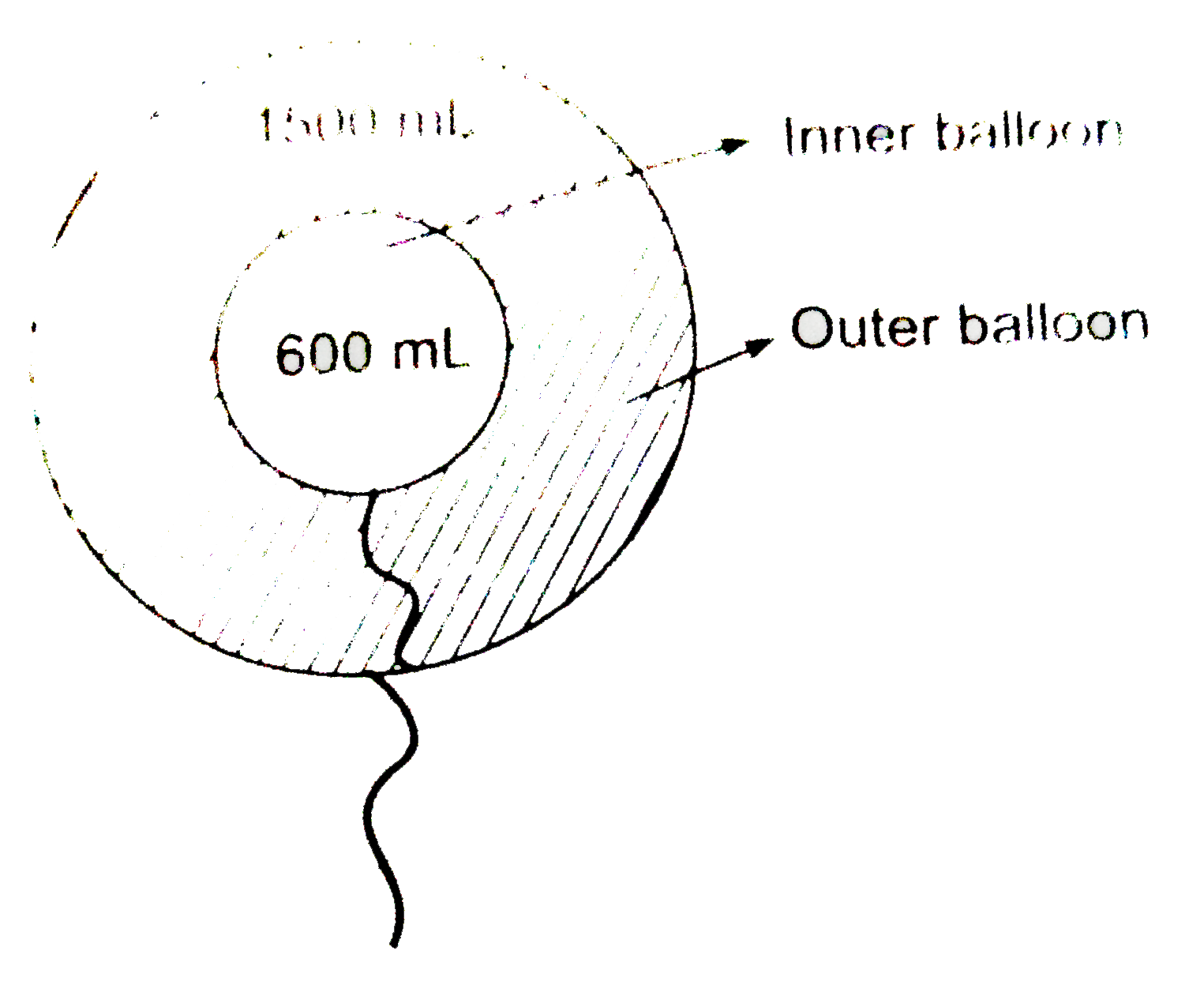A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
STATES OF MATTER
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level-2 (NUMBERICAL VALUE TYPE FOR JEE MAIN|15 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE-Main ( ARCHIVE )|17 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level-1|75 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|50 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY - I
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|31 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-STATES OF MATTER-Level-2
- At point P and Q, the real gas deviation with respect to ideal gas is ...
Text Solution
|
- At what temperature will the molar kinetic energy of 0.3 mol of He be ...
Text Solution
|
- Two inflated ballons I and II (thin skin) having volume 600 mL and 150...
Text Solution
|
- The volume of a gas increases by a factor of 2 while the pressure dec...
Text Solution
|
- Oxygen gas generated by the decomposition of potassium chorate is coll...
Text Solution
|
- A real gas most closely approaches the behaviour of an ideal gas at:
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statement is(are) correct?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements is(are) correct for a gas X having m...
Text Solution
|
- At 47^(@)C and 16.0 atm, the molar volume of NH3 gas is about 10% less...
Text Solution
|
- A gaseous mixture (He and CH(4)) which has density (64)/(246.3) gm/lit...
Text Solution
|
- The graph of P vs V is given at different temperature The correct...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch shows the plot of Z vs P for 1 mol of a hypothetical gas at thr...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch shows the plot of Z vs P for 1 mol of a hypothetical gas at thr...
Text Solution
|
- Sketch shows the plot of Z vs P for 1 mol of a hypothetical gas at thr...
Text Solution
|
- Compressibility factor for H(2) behaving as real gas is
Text Solution
|
- A real gas obeying van der Waals equation will resemble ideal gas , if...
Text Solution
|
- If temperature and volume are same, the pressure of a gas obeying van ...
Text Solution
|
- The critical pressure P(C) and critical temperature T(C) for a gas obe...
Text Solution
|
- For non-zero value of force of attraction between gas molecular at lar...
Text Solution
|
- At Boyle's temperature the value of compressibility factro Z = (PV(m(/...
Text Solution
|