A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
STATES OF MATTER
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level-2 (NUMBERICAL VALUE TYPE FOR JEE MAIN|15 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE-Main ( ARCHIVE )|17 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise Level-1|75 VideosSTATES OF MATTER
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|50 VideosSTOICHIOMETRY - I
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|31 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-STATES OF MATTER-Level-2
- A real gas obeying van der Waals equation will resemble ideal gas , if...
Text Solution
|
- If temperature and volume are same, the pressure of a gas obeying van ...
Text Solution
|
- The critical pressure P(C) and critical temperature T(C) for a gas obe...
Text Solution
|
- For non-zero value of force of attraction between gas molecular at lar...
Text Solution
|
- At Boyle's temperature the value of compressibility factro Z = (PV(m(/...
Text Solution
|
- The critical density of the gas CO(2) is 0.44 g cm^(-3) at a certain t...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is correct for critical temperature ?
Text Solution
|
- The vander waal gas constant 'a' is given by
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is/are correct?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following statements are incorrect?
Text Solution
|
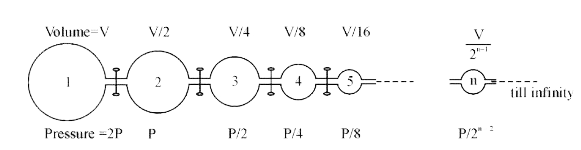
- Infinite number of flask are connected to one another as shown above. ...
Text Solution
|
- Following represents the Maxwell distribution curve for an ideal gas a...
Text Solution
|
- At low pressure the van der Waals' equation is reduced to [P +(a)/(V^(...
Text Solution
|
- Following graph represents a pressure (P) volume (V) relationship at a...
Text Solution
|
- Density of dry air ( only N(2) and O(2)) is 1.24g litre^(-1) at 760 m ...
Text Solution
|
- The root mean square speed of hydrogen is sqrt(5) times than that of n...
Text Solution
|
- A gaseous mixture containing He, CH(4) and SO(2) in 1:2:3 mole ratio, ...
Text Solution
|
- 6 xx 10^(22) gas molecules each of mass 10^(-24) kg are taken in a ve...
Text Solution
|
- Two flask A and B of equal volumes maintained at temperature 300 K and...
Text Solution
|
- The density of gas A is twice that to B at the same temperature. The m...
Text Solution
|