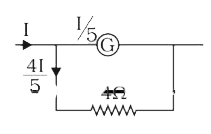
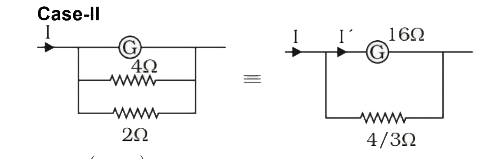
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
DC CIRCUIT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL-2 DAILY TUTORIAL SHEET-4|10 VideosDC CIRCUIT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL-2 DAILY TUTORIAL SHEET-5|10 VideosDC CIRCUIT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL-2 DAILY TUTORIAL SHEET-2|10 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-F|10 VideosDYNAMICS OF A PARTICLE
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advance (Archive) Level - II (SINGLE OPTION CORRECT TYPE )|31 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-DC CIRCUIT-LEVEL-2 DAILY TUTORIAL SHEET-3
- An unknown resistance R(1) is connected is series with a resistance of...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown below, the internal resistance of the cell is neg...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown below, the internal resistance of the cell is neg...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown below, the internal resistance of the cell is neg...
Text Solution
|
- When a galvanometer is shunted with a 4Omega resistance, the deflectio...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a potentiometer circuit, a cell of emf E1 is balanced by...
Text Solution
|
- An unknown resistance R is connected in series with a 2 ohm resistance...
Text Solution
|
- The value of resistance of an unknown resistor is calculated using the...
Text Solution
|
- The value of resistance of an unknown resistor is calculated using the...
Text Solution
|
- The value of resistance of an unknown resistor is calculated using the...
Text Solution
|