A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
DC CIRCUIT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL-1 JEE MAIN ARCHIVE|93 VideosDC CIRCUIT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCED ARCHIVE|68 VideosDC CIRCUIT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL-2 DAILY TUTORIAL SHEET-4|10 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-F|10 VideosDYNAMICS OF A PARTICLE
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advance (Archive) Level - II (SINGLE OPTION CORRECT TYPE )|31 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-DC CIRCUIT-LEVEL-2 DAILY TUTORIAL SHEET-5
- A battery has a variable EMF E depending on the amount of electrochemi...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, the internal resistances of the batteries are in...
Text Solution
|
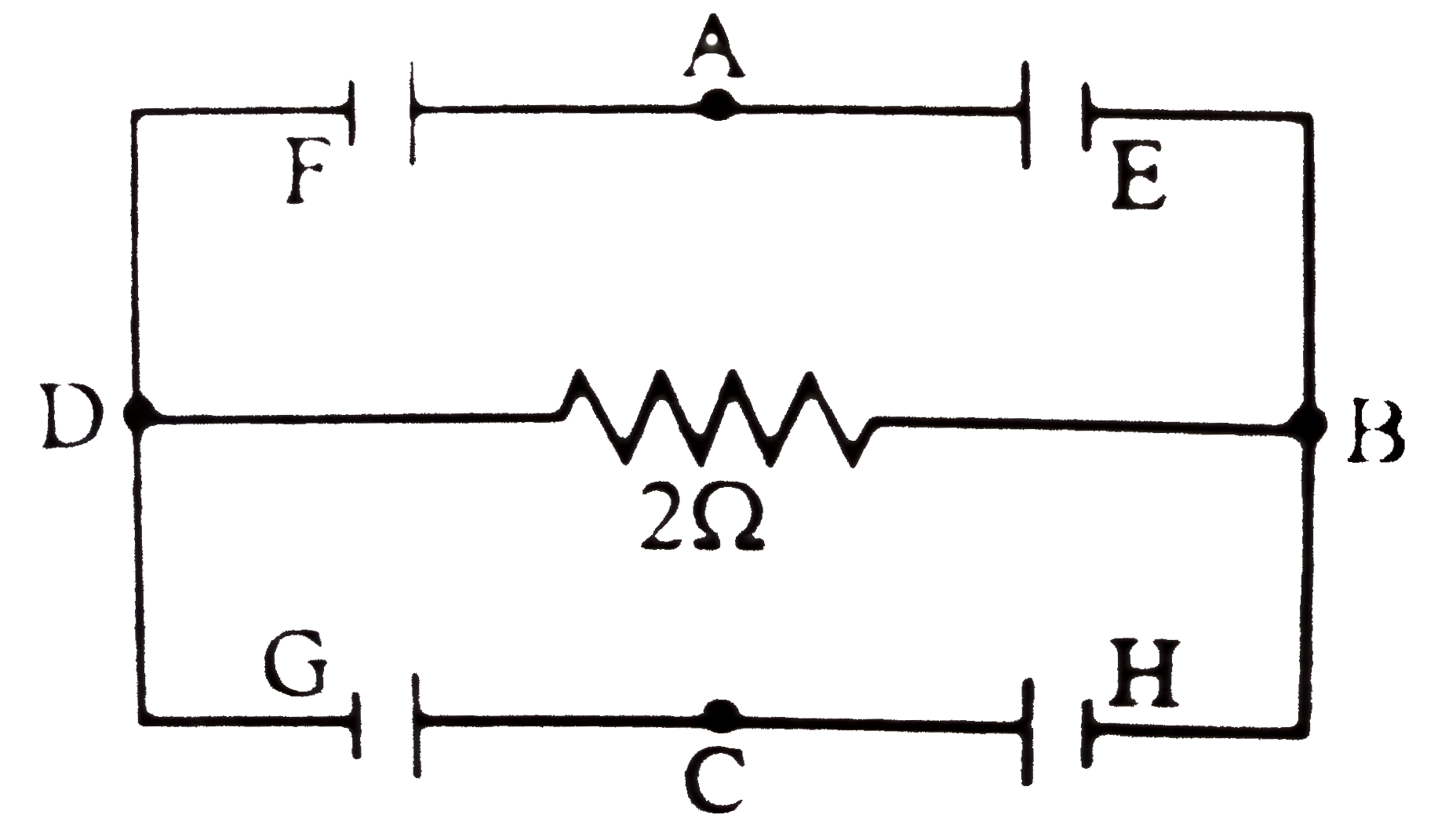
- In the circuit shown E, F, G and H are cells of emf 2V, 1V, 3V and 1V ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, the battery, the ammeter and the voltmeter are i...
Text Solution
|
- A voltmeter of resistance 100 Omega connected to the terminals of a ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown, the length of AB is 100 cm. The lengthj1 for wh...
Text Solution
|
- Four bulbs are connected as shown to a battery of EMF 220 V. The volta...
Text Solution
|
- In the given network, if an ideal battery is connected between points ...
Text Solution
|
- Can conductivity alone be used to compare the conductance of (i) metal...
Text Solution
|
- In the given circuit, currents through 4 Omega and 10 Omega resist...
Text Solution
|