Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-DC CIRCUIT-JEE ADVANCED ARCHIVE
- In the circuit, a voltmeter reads 30 V when it is connected across 400...
Text Solution
|
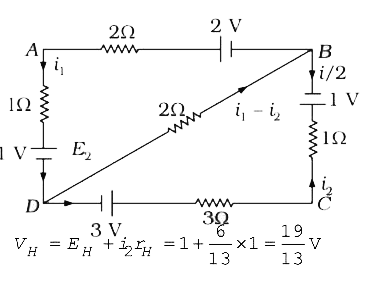
- In the circuit in figure E1=3V, E2=2V, E3=1V and R=r1=r2=r3=1Omega ...
Text Solution
|
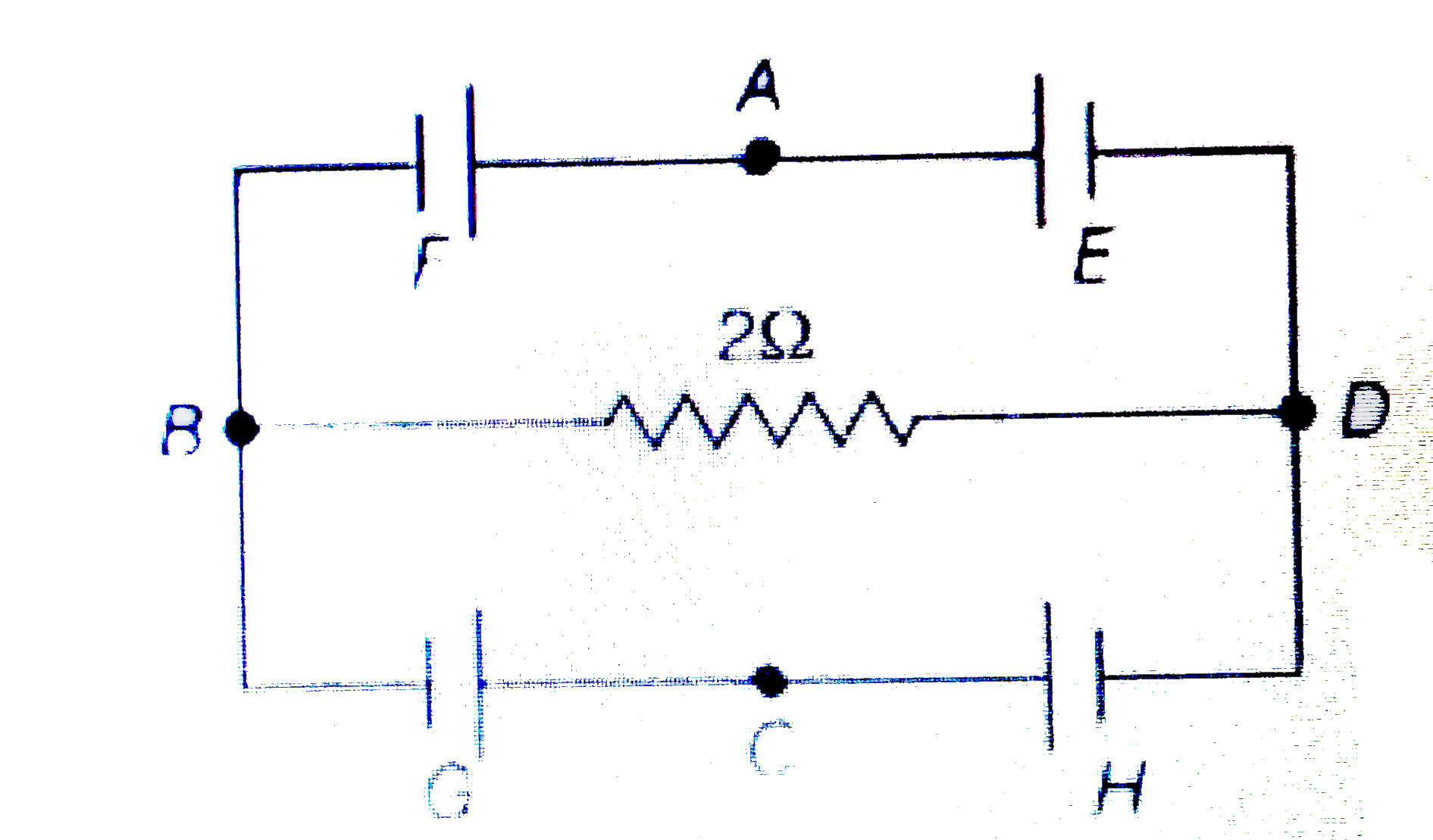
- In the circuit shown, E, F, G and H are cells of emf 2V, 1V, 3V and 1V...
Text Solution
|
- An infinite ladder is constructed with 1(Omega)and 2(Omega)resistor as...
Text Solution
|
- An electrical circuit is shown in figure. Calculate the potential diff...
Text Solution
|
- Find the emf (V) and internal resistance (R) of a single battery which...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform wire AB of length 1 m, an unknown resistance X, and a r...
Text Solution
|
- When two identical batteries of internal resistance 1Omega each are co...
Text Solution
|
- Two batteries of different emfs and different internal resistances are...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer gives full scale deflection with 0.006 A current. By co...
Text Solution
|
- In the following circuit, the current through the resistor R (=2Omega)...
Text Solution
|
- Two resistors 400Omega and 800Omega are connected in series with a 6 V...
Text Solution
|
- An electric bulb rated for 500 W at 100 V is used in a circuit having ...
Text Solution
|
- In the circuit shown in figure , each battery is 5 V and has an intern...
Text Solution
|
- The equivalent resistance between points A and B of the circuit given ...
Text Solution
|
- A 25W and 100W bulbs are joined in series and connected to the mains. ...
Text Solution
|
- When a steady current passes through a cylindrical conductor, is there...
Text Solution
|
- Determine True or False. Electrons in a conductor have no motion in th...
Text Solution
|
- The current - voltage graphs for a given metallic wire at two differen...
Text Solution
|
- We can use a rheostat as a potential divider.
Text Solution
|