A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ROTATIONAL MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive) (SINGLE OPTION CORRECT TYPE)|26 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive) (MULTIPLE OPTIONS CORRECT TYPE)|17 VideosROTATIONAL MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 2 (Angular Momentum, Collision)|20 VideosREVISION TEST-2 JEE
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise PHYSICS|25 VideosSIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise 7-previous year question|46 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-ROTATIONAL MOTION -JEE MAIN (ARCHIVE)
- A solid sphere of mass m & rdius R is divided in two parts of m mass (...
Text Solution
|
- A metal coinn of mass 5 g and radius 1 cm is fixed to a thin stick AB...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc of radius b has a hole of radius a at its centre (see ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length l is being rotated in a horizontal plane with ...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth wire of length 2pir is bent into a circle and kept in a vert...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length 50cm is pivoted at one end. It is raised such that if ...
Text Solution
|
- An L-shaped object, made of thin rods of uniform mass density, is susp...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid massless rod of length 3l has two masses attached at each end ...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical spherical balls of mass M and radius R each are stuck on...
Text Solution
|
- A homogenous solid cylindrical roller of radius R and mass M is pulled...
Text Solution
|
- To mop-clean a floor, a cleaning machine presses a circular mop of rad...
Text Solution
|
- A string is wound around a hollow cylinder of mass 5 Kg and radius ...
Text Solution
|
- A circular disc D(1) of mass M and radius R has two identical disc D(...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude of torque on a particle of mass 1 kg is 2.5 Nm about t...
Text Solution
|
- An equilateral triangle ABC is cut from a thin solid sheet of wood .(s...
Text Solution
|
- A slab is subjected to two forces vec F(1) and vec F(2) of same magnit...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 20 g is released with an initial velocity 5m//s alo...
Text Solution
|
- The moment of inertia of a solid sphere, about an axis parallel to its...
Text Solution
|
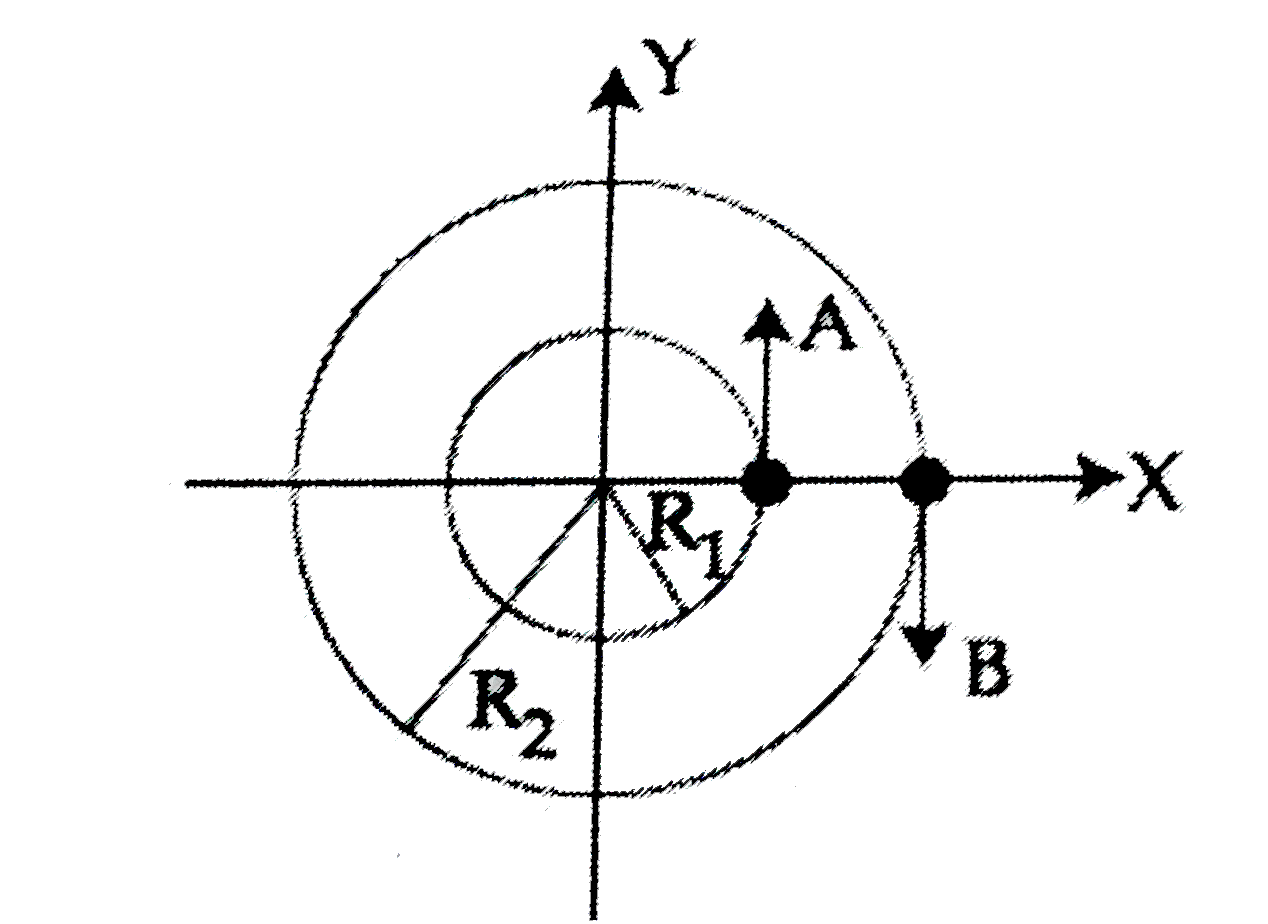
- Two particles A,B are moving on two concentric circles of radii R1 and...
Text Solution
|
- Let the moment of inertia of a hollow cylinder of length 30 cm (...
Text Solution
|