Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 0 (LONG ANSWER TYPE )|8 VideosELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 1|105 VideosELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|89 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION & ALTERNATIVE CURRENT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|52 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE) - TRUE/FALSE TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-ELECTROSTATICS-LEVEL - 0 (SHORT ANSWER TYPE )
- A point charge Q is placed at the point O as shown in Fig. Is the po...
Text Solution
|
- A small sphere of radius r(1) and charge q(1) is enclosed by a spheric...
Text Solution
|
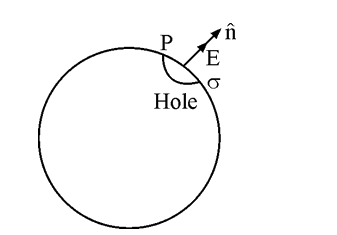
- A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface. Show ...
Text Solution
|
- A polythene piece rubbed with wool is found to have a negative charge ...
Text Solution
|
- Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black bo...
Text Solution
|
- Careful measurement of the electric field at the surface of a black bo...
Text Solution
|
- An infinite cylinder of radius r(o), carrying linear charge density la...
Text Solution
|
- Two metal spheres, one of radius R and the other of radius 2R, both ha...
Text Solution
|
- A long charged cylinder of linear charge density lambda is surrounde...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a uniform electric field E = 3xx10^(3) hat(i) N//C. (a) What...
Text Solution
|
- Consider vec(E)=3xx10^(3) hat(i) (N//C) then what is the flux through ...
Text Solution
|
- State Gauss’s law in electrostatics. A cube with each side a is kept i...
Text Solution
|
- Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On ...
Text Solution
|
- Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On ...
Text Solution
|
- Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On ...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges -q each are fixed separated by distance 2d. A third charge...
Text Solution
|
- Describe schematically the equipotential surfaces corresponding to (...
Text Solution
|
- Draw 3 equipotential surfaces corresponding to a field that uniformly ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe schematically the equipotential surfaces corresponding to ...
Text Solution
|
- Geeta has dry hair. A comb ran through her dry hair attracts small bit...
Text Solution
|