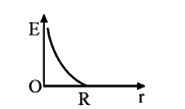
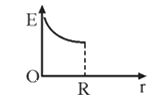
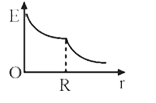
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE MAIN|65 VideosELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|89 VideosELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 1|105 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION & ALTERNATIVE CURRENT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|52 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE) - TRUE/FALSE TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-ELECTROSTATICS-LEVEL - 2
- The dipole moment of a system of charge +q distributed uniformly on an...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a nonconducting ring which has positive and negative ...
Text Solution
|
- Along the x-axis, three charges q/2,-q and q/2 are placed at x=0,x=a ...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole is placed at the centre of a hollow conducting sphe...
Text Solution
|
- For the situation shown in the figure (r gt gt length of dipole) mark ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two electric dipoles P(1) and P(2) placed at (0, 0) and (1,...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two electric dipoles P(1) and P(2) placed at (0, 0) and (1,...
Text Solution
|
- Consider two electric dipoles P(1) and P(2) placed at (0, 0) and (1,...
Text Solution
|
- A thin non-conducting ring or radius a has a linear charge density lam...
Text Solution
|
- A large sheet carries uniform surface charge density sigma. A rod of l...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic spherical shell of radius R has a charge -Q on it. A point...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric conducting spheres of radii R and 2R are crrying charge...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical conducting spheres, fixed in space, attract each other w...
Text Solution
|
- There are four concentric shells A, B, C and D of radii a,2a,3a and 4a...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting sphere of radius R(2) has a spherical cavity of radius R...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting sphere of radius R(2) has a spherical cavity of radius R...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting sphere of radius R(2) has a spherical cavity of radius R...
Text Solution
|
- For the situation shown in (fig. 3.147), mark the correct statement (s...
Text Solution
|
- Three identical metallic plates are kept parallel to one another at se...
Text Solution
|
- Two refracting media are separated by a spherical interface as shown i...
Text Solution
|