A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|89 VideosELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 2|60 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION & ALTERNATIVE CURRENT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|52 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE) - TRUE/FALSE TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-ELECTROSTATICS-JEE MAIN
- Two positive charges of magnitude q are placed at the ends of a side (...
Text Solution
|
- The potential in the electric field varies as V = -a x^2 + b with resp...
Text Solution
|
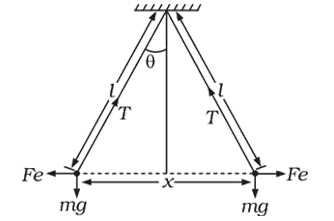
- Two identical charged spheres suspended from a common point by two mas...
Text Solution
|
- In a uniformly charged sphere of total charge Q and radius R, the elec...
Text Solution
|
- An insulating solid sphere of radius R has a uniformly positive charge...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is uniformly distributed over a long rod AB of length L as ...
Text Solution
|
- Two charges, each equal to q, are kept at x = −a and x = a on the x-ax...
Text Solution
|
- Assume that an electric fieldvecE = 30 x^(2)hati exists in space. Then...
Text Solution
|
- A long cylindrical shell carries positive surface charge sigma in the ...
Text Solution
|
- A uniformly charged solid sphere of radius R has potential V(0) (meas...
Text Solution
|
- The region between two concentric spheres of radii a and b (gt a) cont...
Text Solution
|
- An electric dipole has a fixed dipole moment vecp, which makes angle t...
Text Solution
|
- Three concentric spherical metallic shells A, B and C of radii a, b an...
Text Solution
|
- Charge is distributed within a sphere of radius R with a volume charge...
Text Solution
|
- Two point charges q(1)(sqrt(10)mu C) and q(2)(-25mu C) are placed on t...
Text Solution
|
- Three charges +Q, q, +Q are placed respectively, at distance, 0, d...
Text Solution
|
- For a uniformly charged ring of radius R, the electric field on its ex...
Text Solution
|
- Charges -q and +q located at A and B, respectively, constitute an elec...
Text Solution
|
- Four equal point charges Q each are placed in the xy plane at (0,2), (...
Text Solution
|
- A charge Q is distributed over three concentric spherical shells of ra...
Text Solution
|