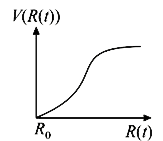
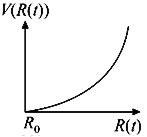
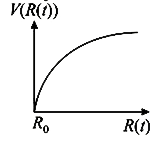
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE Advanced (Archive)|89 VideosELECTROSTATICS
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise LEVEL - 2|60 VideosELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION & ALTERNATIVE CURRENT
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|52 VideosENERGY & MOMENTUM
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise JEE ADVANCE (ARCHIVE) - TRUE/FALSE TYPE|1 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-ELECTROSTATICS-JEE MAIN
- Two electric dipoles, A, B with respective dipole moments vec(d(A))=-4...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m and charge q is in a electric and magnetic f...
Text Solution
|
- An electric field of 1000 V//m is applied to an electric dipole at an...
Text Solution
|
- Three charges Q+q and + q are placed at the vertices of a right -angle...
Text Solution
|
- The given graph shows variation (with distance r form center) of :
Text Solution
|
- There is a uniform spherically symmetric surface charge density at a ...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the electric dipole moment of the syatem of three charg...
Text Solution
|
- The bob of a simple pendulum has mass 2g and a charge of 5.0muC. It is...
Text Solution
|
- A solid conducting sphere, having a charge Q, is surrounded by an unch...
Text Solution
|
- A positive charge is released from rest at a distance r(0) from a posi...
Text Solution
|
- In Region of Electric field Given by vec(E)=(Ax-B)hat(I). Where A=20 u...
Text Solution
|
- A electric dipole is in equilibrium having charge q and -q are placed ...
Text Solution
|
- A system of three charges are placed as shown in the figure : If ...
Text Solution
|
- Four points charges -q,+q,+q and -q are placed on y-axis at y=-2d, y=-...
Text Solution
|
- A particle A of charge 1 mu C is held fixed at a point P in free spa...
Text Solution
|
- A simple pendulum of length L is placed between the plates of a parall...
Text Solution
|
- A Circular ring of radius 3a is uniformly charged with charge q is kep...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of radius R has total charge 2Q and volume charge densi...
Text Solution
|
- Shown in the figure is a shell made of a conductor. It has inner radiu...
Text Solution
|
- A point dipole vecp=-p(0)xhatx is kept at the origin. The potential an...
Text Solution
|