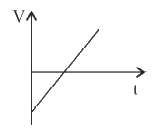
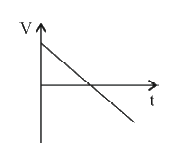
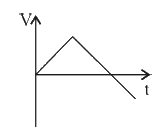
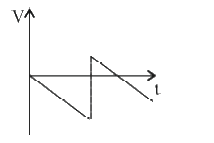
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE & PLANE
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise EFFICIENT|50 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE & PLANE
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|52 VideosMOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE & PLANE
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IMPECCABLE|52 VideosMOCK TEST 9
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise PHYSICS (SECTION 2)|5 VideosMotion in Straight Line
VMC MODULES ENGLISH|Exercise IN-CHAPTER EXERCISE-J|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-MOTION IN A STRAIGHT LINE & PLANE -ENABLE
- A bullet is fired from a gun eith a speed of 1000m/s on order to hit t...
Text Solution
|
- From a tower of height H, a particle is thrown vertically upwards with...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet losses 1/n of its velocity in passing through a plank. What i...
Text Solution
|
- The relation between time t and distance x t= ax^(2) +bx is , where a...
Text Solution
|
- If acceleration a(t) = 3t^(2) and initial velocity u=0 m/s , then the ...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity of any particle is related with its displacement As, x = ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle moves in a straight line with retardation proportional to i...
Text Solution
|
- An object moving with a speed of 6.25 m//s is declerated at a rate g...
Text Solution
|
- A particle falls from a height h and rebounds to a height h (1) ( h (1...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity-time plot for a particle moving on a straight line is sh...
Text Solution
|
- For the displacement-time graph shown in figure, the ratio of the magn...
Text Solution
|
- The displacement-time graph of a moving object is shown in figure. Whi...
Text Solution
|
- A particles starts from rest. Its acceleration (a) versus time (t) is ...
Text Solution
|
- Velocity of boat in still water is 13 m/s. If water flows ina river wi...
Text Solution
|
- The uniform motion in the following acceleration-time graph is
Text Solution
|
- The following shows the velocity-timegraphfor a moving object. The max...
Text Solution
|
- Rain is falling vertically downward with velocity 4 m//s. A man is mov...
Text Solution
|
- A boat man could row his boat with a speed 10 m/sec. He wants to take ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle located at x = 0 at time t = 0, starts moving along with t...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a rubber ball freely falling from a height h = 4.9 m onto a h...
Text Solution
|