Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
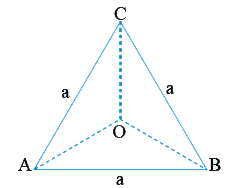
- ABC is an equilateral triangle. Length of each side is 'a' and centroi...
Text Solution
|
- Taken on side vec AC of a triangle ABC, a point M such that vec AM=(1)...
Text Solution
|
- If D is the mid-point of the side B C of a triangle A B C , prove that...
Text Solution
|
- Given an equilateral triangle ABC with side length equal to 'a'. Let M...
Text Solution
|
- If D is the mid point of side BC of a triangle ABC such that vec A B+...
Text Solution
|
- Let G be the centroid of Delta ABC , If vec(AB) = vec a , vec(AC) = v...
Text Solution
|
- यदि त्रिभुज ABC समबाहु हो तथा सदिश vec(AB) एवं vec(BC) एकक सदिश हो...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is an equilateral triangle. Length of each side is 'a' and centroi...
Text Solution
|
- ABC একটি সমবাহু ত্রিভুজ। O ত্রিভুজটির ভরকেন্দ্র। vec(AB)+vec(AC)=nvec(...
Text Solution
|