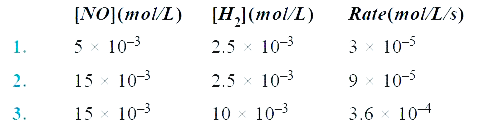A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- For a reaction 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) to N2(g) + 2H2O(g) , the following data...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) to N2(g) + 2H2O(g) , the following data...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) to N2(g) + 2H2O(g) , the following data...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) to N2(g) + 2H2O(g) , the following data...
Text Solution
|
- Write the equilibrium constant expressions for the following reactions...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) to N2(g) + 2H2O(g) , the following data...
Text Solution
|
- For a reaction 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) to N2(g) + 2H2O(g) , the following data...
Text Solution
|
- निम्न अभिक्रिया, 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) rarr N2(g) + 2H2O(g) इसमें नि...
Text Solution
|
- For the following reaction, 2H2 +2NO hArr 2H2 O +N2 the following rate...
Text Solution
|