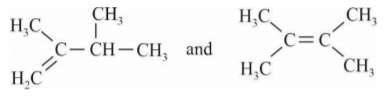
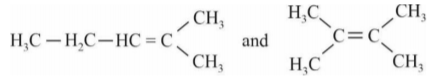
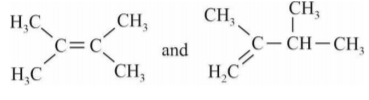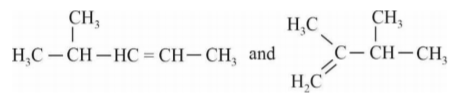A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
VMC MODULES ENGLISH-MOCK TEST 3-PART II : CHEMISTRY (SECTION - 2)
- When 3,3-Dimethyl-2-butanol is heated with acid H(3)PO(4), it is con...
Text Solution
|
- For the order reaction, A((g))to 3B((g)) the concentration versus time...
Text Solution
|
- The number of asymmetric centres present in the following compound are...
Text Solution
|
- An ideal solution is formed by mixing of 460 g. of ethanol with xg. of...
Text Solution
|
- A 0.0020 m aqueous solution of an ionic compound Co(NH(3))(5)(NO(2))Cl...
Text Solution
|
- A 20 ml solution containing 0.2 g impure H(2)O(2) reacts completely ...
Text Solution
|
- The mass of dinitrogen in grams produced by the thermal decomposition ...
Text Solution
|
- Amongst given polymers, how many of them are addition polymer. (i)...
Text Solution
|
- The maximum allowed concentration in ppm of zinc in drinking water
Text Solution
|
- The Reagent which is commercially known as ‘calgon’ that is used to re...
Text Solution
|
- The total number of distinct naturally occuring essential amino acids ...
Text Solution
|