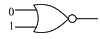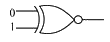To determine which of the given gates will have an output of 1, we will analyze each gate's truth table step by step.
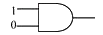
### Step 1: Analyze the AND Gate
1. **Truth Table for AND Gate:**
- Inputs: A, B
- Output: C
- The output of an AND gate is 1 only when both inputs are 1.
- Truth Table:
- A = 0, B = 0 → C = 0
- A = 0, B = 1 → C = 0
- A = 1, B = 0 → C = 0
- A = 1, B = 1 → C = 1
2. **Conclusion for AND Gate:**
- For inputs (0, 1), the output is 0. Thus, the AND gate does not give an output of 1.
### Step 2: Analyze the NOR Gate
1. **Truth Table for NOR Gate:**
- Inputs: A, B
- Output: C
- The output of a NOR gate is 1 only when both inputs are 0.
- Truth Table:
- A = 0, B = 0 → C = 1
- A = 0, B = 1 → C = 0
- A = 1, B = 0 → C = 0
- A = 1, B = 1 → C = 0
2. **Conclusion for NOR Gate:**
- For inputs (0, 1), the output is 0. Thus, the NOR gate does not give an output of 1.
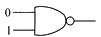
### Step 3: Analyze the NAND Gate
1. **Truth Table for NAND Gate:**
- Inputs: A, B
- Output: C
- The output of a NAND gate is 1 unless both inputs are 1.
- Truth Table:
- A = 0, B = 0 → C = 1
- A = 0, B = 1 → C = 1
- A = 1, B = 0 → C = 1
- A = 1, B = 1 → C = 0
2. **Conclusion for NAND Gate:**
- For inputs (0, 1), the output is 1. Thus, the NAND gate gives an output of 1.
### Step 4: Analyze the XNOR Gate
1. **Truth Table for XNOR Gate:**
- Inputs: A, B
- Output: C
- The output of an XNOR gate is 1 when both inputs are the same.
- Truth Table:
- A = 0, B = 0 → C = 1
- A = 0, B = 1 → C = 0
- A = 1, B = 0 → C = 0
- A = 1, B = 1 → C = 1
2. **Conclusion for XNOR Gate:**
- For inputs (0, 1), the output is 0. Thus, the XNOR gate does not give an output of 1.
### Final Conclusion:
- The only gate that gives an output of 1 for the input combination (0, 1) is the **NAND gate**.