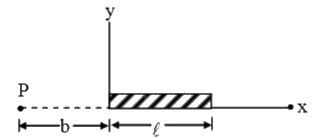
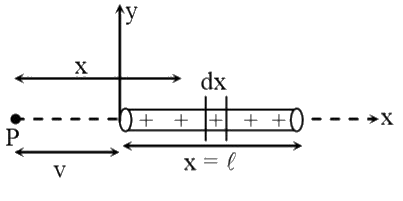
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A rod of length 'l' is placed along x-axis. One of its ends is at the...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length L lies along the x-axis with its left end at the origi...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l, has a uniform positive charge per unit length and a...
Text Solution
|
- A non-uniform thin rod of length L is palced along X-axis so that one ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod length L and mass M is placed along the x-axis with one end at t...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the potential due to a thin uniformly charged rod of length ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length L is placed along the x-axis between x = 0 and x = L. ...
Text Solution
|
- A non–uniform thin rod of length L is placed along x-axis as such its ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length l is placed along x - axis. One of its ends is at the ...
Text Solution
|