A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CIRCLES
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Section-I (Solved MCQs)|1 VideosCIRCLES
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Section II - Assertion Reason Type|12 VideosCIRCLES
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|53 VideosCARTESIAN PRODUCT OF SETS AND RELATIONS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|30 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|58 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH-CIRCLES-Section I - Solved Mcqs
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- If AB is the intercept of the tangent to the circle x^2 +y^2=r^2 betwe...
Text Solution
|
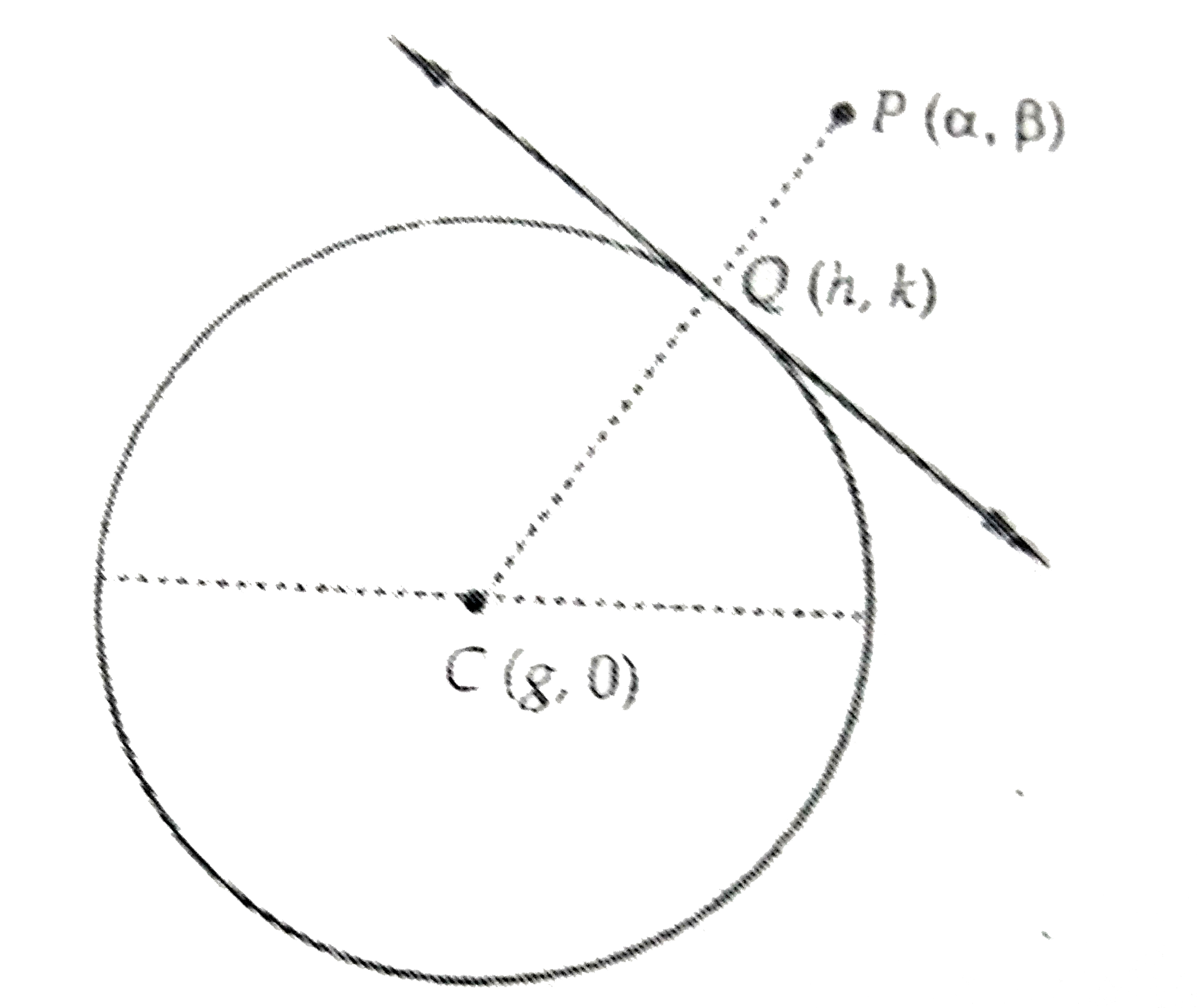
- The locus of the foot of the normal drawn from any point P(alpha, beta...
Text Solution
|
- The chords of contact of the pair of tangents drawn from each point on...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a circle C1 is x^2+y^2-4x-2y-11=0 A circleC2 of radius...
Text Solution
|
- If a chord of contact of tangents drawn from a point P with respect to...
Text Solution
|
- If (a, 0) is a point on a diameter of the circle x^(2)+y^(2)=4, then t...
Text Solution
|
- If the polar of a point ( p,q) with respect to the circle x^(2)+ y^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- The locus of the mid-points of the chords of the circle of lines radiÃ...
Text Solution
|
- If two circles and a(x^2 +y^2)+bx + cy =0 and p(x^2+y^2)+qx+ry= 0 touc...
Text Solution
|
- The circles x^(2)+y^(2)+2x-2y+1=0 and x^(2)+y^(2)-2x-2y+1=0 touch each...
Text Solution
|
- The point of intersection of the common chords of three circles descri...
Text Solution
|
- If P and Q are the points of intersection of the circles x^(2)+y^(2)+3...
Text Solution
|
- If the chord of contact of tangents from a point P to a given circle p...
Text Solution
|
- If one of the circles x^2+y^2+2ax+c=0 and x^2+y^2+2bx+c=0 lies within ...
Text Solution
|
- The chord of contact of tangents from a point P to a circle passes thr...
Text Solution
|
- The locus of the centre of circle which cuts off an intercept of const...
Text Solution
|
- Let PQ and RS be tangents at the extremities of the diameter PR of a c...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- A tangent to the circle x^(2)+y^(2)=1 through the point (0, 5) cuts t...
Text Solution
|