A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
CIRCLES
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Section-I (Solved MCQs)|1 VideosCIRCLES
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Section II - Assertion Reason Type|12 VideosCIRCLES
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|53 VideosCARTESIAN PRODUCT OF SETS AND RELATIONS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|30 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|58 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH-CIRCLES-Section I - Solved Mcqs
- From a point A(1, 1) on the circle x^(2)+y^(2)-4x-4y+6=0 two equal cho...
Text Solution
|
- The number of circles belonging to the system of circles 2(x^(2)+y^(2)...
Text Solution
|
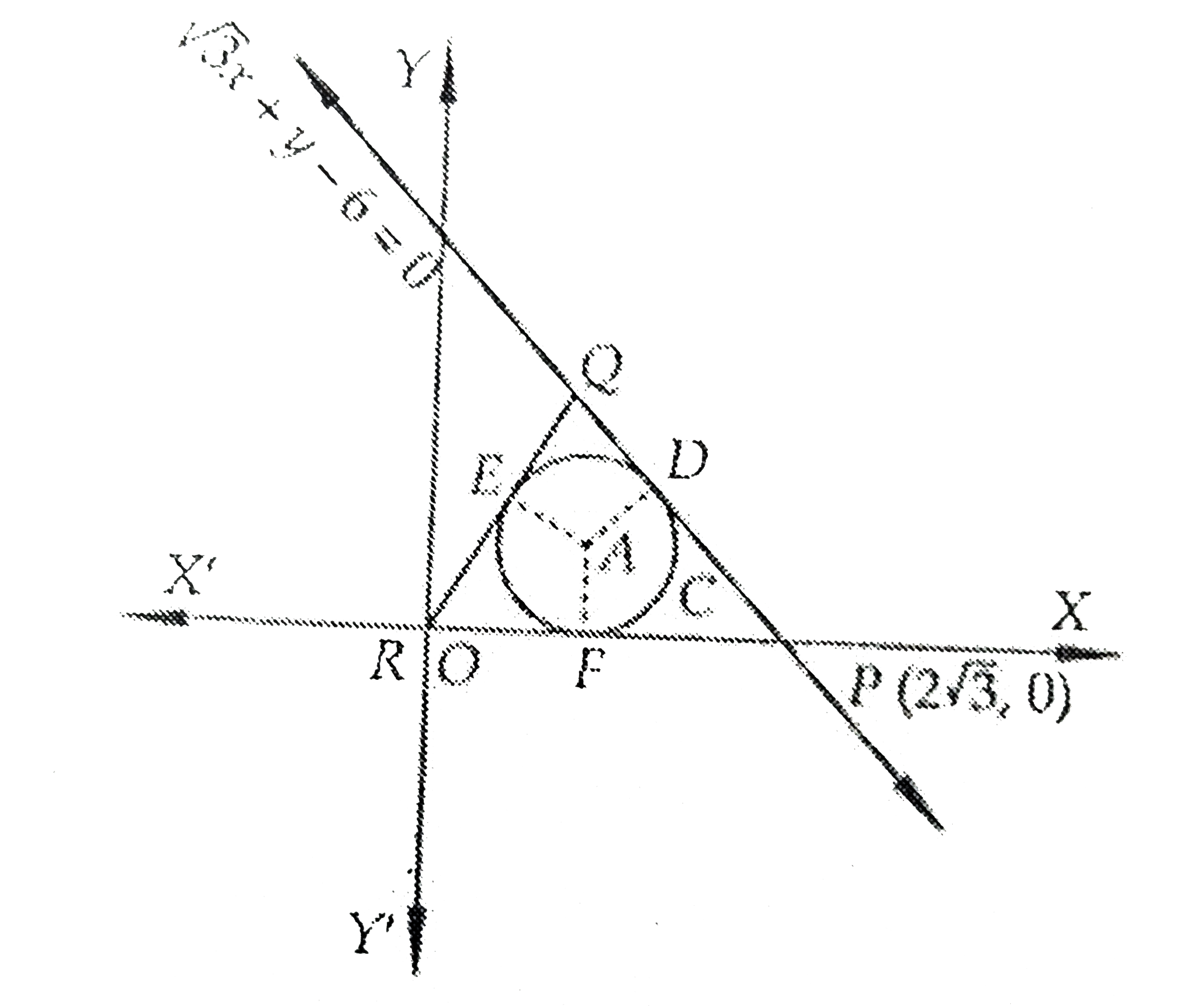
- A circle C of radius 1 is inscribed in an equilateral triangle PQR. Th...
Text Solution
|
- If D,E and F are respectively, the mid-points of AB,AC and BC in Delta...
Text Solution
|
- In example 70, equations of the sides QR and RP are respectively
Text Solution
|
- A point on the line x=4 from which the tangents drawn to the circle 2(...
Text Solution
|
- The tangents PA and PB are drawn from any point P of the circle x^(2)+...
Text Solution
|
- Two concentric circles of which smallest is x^(2)+y^(2)=4, have the di...
Text Solution
|
- If the circle x^2+y^2=a^2 intersects the hyperbola x y=c^2 at four poi...
Text Solution
|
- If two distinct chords, drawn from the point (p, q) on the circle x^2+...
Text Solution
|
- Let a and b be bonzero real numbers. Then the equation (ax^(2)+by^(2)+...
Text Solution
|
- If the circles x^2+y^2+2a x+c y+a=0 and points Pa n dQ , then find the...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- If a >2b >0, then find the positive value of m for which y=m x-bsqrt(1...
Text Solution
|
- A circle circumscribing an equilateral triangle with centroid at (0,0)...
Text Solution
|
- Consider four circles (x+-1)^2+(y+-1)^2=1 . Find the equation of the s...
Text Solution
|
- The radius of a circle is 20 cm. It is divided into four parts of e...
Text Solution
|
- If circles x^(2)+y^(2)+2x+2y+c=0 and x^(2)+y^(2)+2ax+2ay+c=0 where c i...
Text Solution
|
- A circle is passing through the points A (1, 1) and B (1, 3) and the b...
Text Solution
|
- The equation of a circle which touches the line y = x at (1 , 1) and ...
Text Solution
|