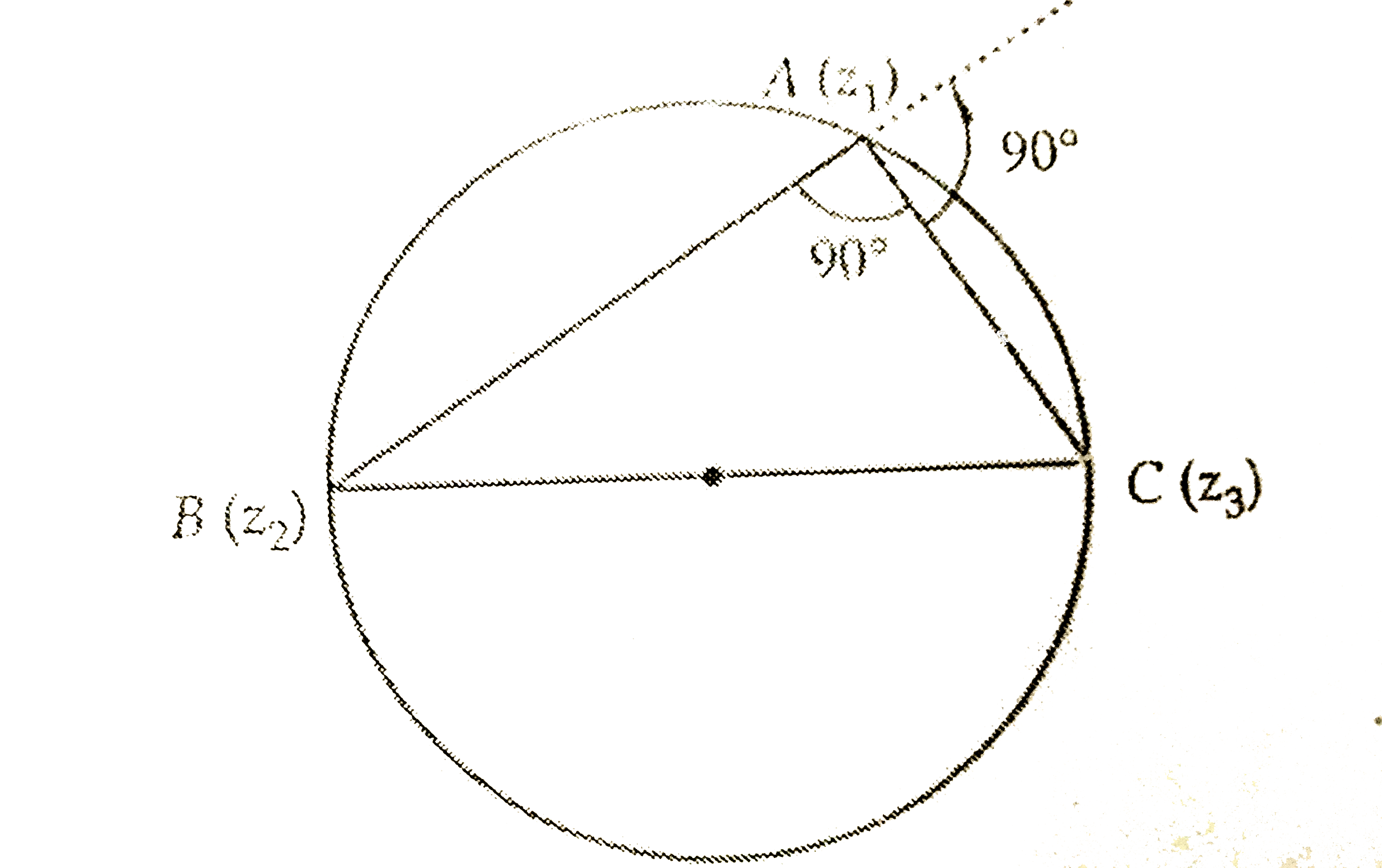A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Section II - Assertion Reason Type|15 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|129 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|58 VideosCIRCLES
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|53 VideosCONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|87 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH-COMPLEX NUMBERS -Section I - Solved Mcqs
- Let P(e^(itheta1)), Q(e^(itheta2)) and R(e^(itheta3)) be the vertices...
Text Solution
|
- If A(z(1)),B(z(2)), C(z(3)) are the vertices of an equilateral triangl...
Text Solution
|
- If A (z1), B (z2) and C (z3) are three points in the argand plane whe...
Text Solution
|
- If a1,a2 ...an are nth roots of unity then1/(1-a1) +1/(1-a2)+1/(1-a3)....
Text Solution
|
- Let A(z(1)) and B(z(2)) be such that angleAOB=theta('O') being the ori...
Text Solution
|
- If one root of z^2 + (a + i)z+ b +ic =0 is real, where a, b, c in R , ...
Text Solution
|
- If A and B represent the complex numbers z(1) and z(2) such that |z(1)...
Text Solution
|
- If z1ne-z2 and |z1+z2|=|1/z1 + 1/z2| then :
Text Solution
|
- Let O, A, B be three collinear points such that OA.OB=1. If O and B re...
Text Solution
|
- If z(0),z(1) represent points P and Q on the circle |z-1|=1 taken in a...
Text Solution
|
- The center of a square ABCD is at the origin and point A is reprsented...
Text Solution
|
- The value of k for which the inequality | Re (z) | + | Im (z)| leq l...
Text Solution
|
- The value of lambda for which the inequality |z(1)/|z(1)|+z(2)/|z(2)||...
Text Solution
|
- If z1a n dz2 both satisfy z+ z =2|z-1| and a r g(z1-z2)=pi/4 , then f...
Text Solution
|
- If z satisfies |z+1|lt|z-2|, then v=3z+2+i satisfies:
Text Solution
|
- If z complex number satisfying |z-1| = 1, then which of the followin...
Text Solution
|
- If z(1),z(2),z(3) are the vertices of an isoscles triangle right angle...
Text Solution
|
- Show that all the roots of the equation a(1)z^(3)+a(2)z^(2)+a(3)z+a(4)...
Text Solution
|
- If |z-1|=1, where z is a point on the argand plane, show that(z-2)/(z)...
Text Solution
|
- Let z be a non-real complex number lying on |z|=1, prove that z=(1+i...
Text Solution
|