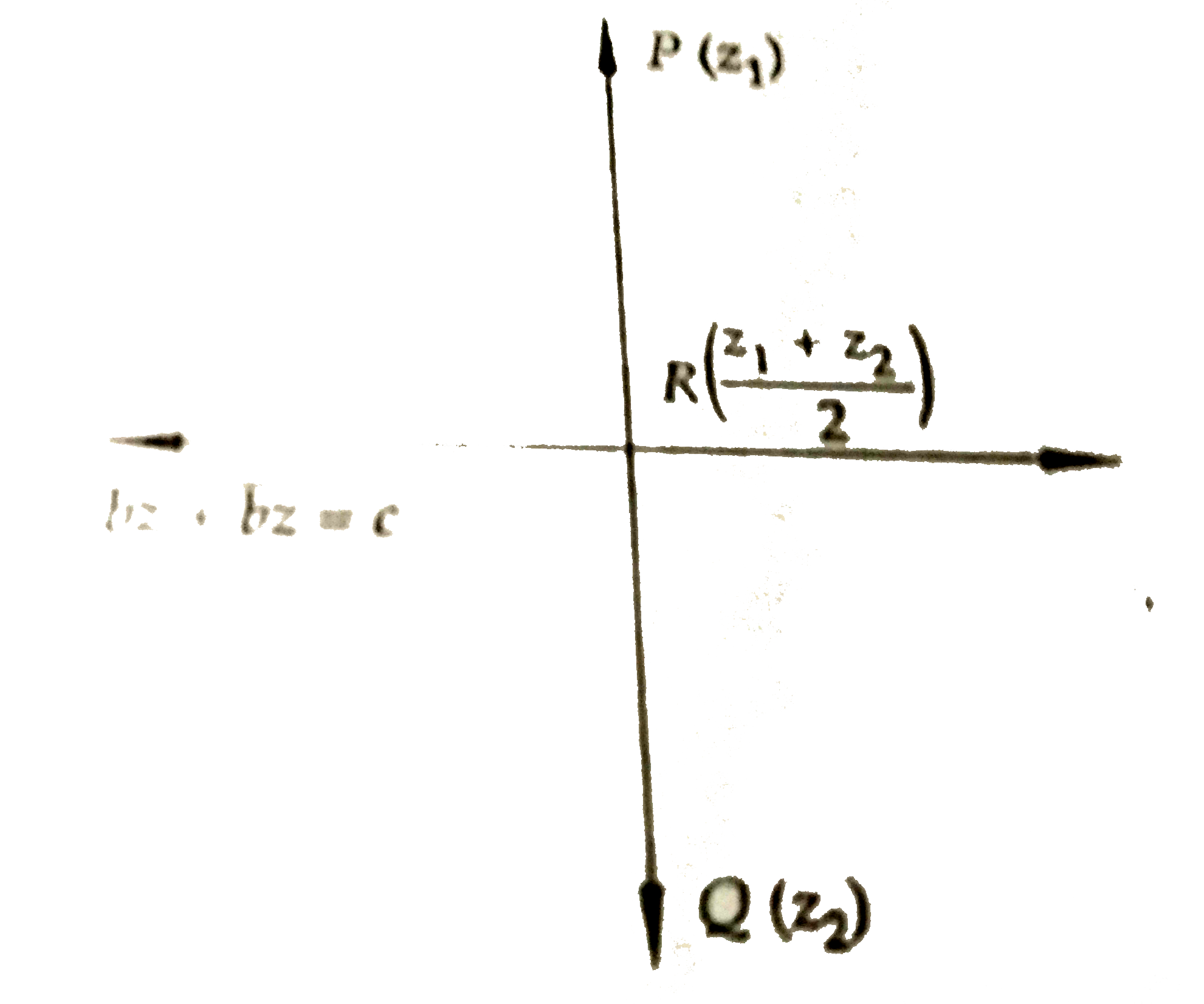A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Section II - Assertion Reason Type|15 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|129 VideosCOMPLEX NUMBERS
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|58 VideosCIRCLES
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Chapter Test|53 VideosCONTINUITY AND DIFFERENTIABILITY
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise|87 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
OBJECTIVE RD SHARMA ENGLISH-COMPLEX NUMBERS -Section I - Solved Mcqs
- If |z|=2 and locus of 5z-1 is the circle having radius a and z1^2+z2^2...
Text Solution
|
- If |z+barz|+|z-barz|=8, then z lies on
Text Solution
|
- If a point z(1) is the reflection of a point z(2) through the line b b...
Text Solution
|
- If z is a complex number satisfying |z^(2)+1|=4|z|, then the minimum v...
Text Solution
|
- If z(1) and z(2) are two complex numbers satisying the equation. |(i...
Text Solution
|
- If alpha is an imaginary fifth root of unity, then log(2)|1+alpha+alph...
Text Solution
|
- The roots of the equation (1+isqrt(3))^(x)-2^(x)=0 form
Text Solution
|
- If |z|=1 and w=(z-1)/(z+1) (where z!=-1), then R e(w) is 0 (b) 1/(|...
Text Solution
|
- about to only mathematics
Text Solution
|
- Let OP.OQ=1 and let O,P and Q be three collinear points. If O and Q re...
Text Solution
|
- If |z|=1a n dz!=+-1, then all the values of z/(1-z^2) lie on a line no...
Text Solution
|
- Let A,B and C be three sets of complex numbers as defined below: {:(,A...
Text Solution
|
- Let S=S1 nn S2 nn S3, where s1={z in C :|z|<4}, S2={z in C :ln[(z-...
Text Solution
|
- In Q.no. 88, if z be any point in A frown B frown C and omega be any p...
Text Solution
|
- A particle P starts from the point z0=1+2i , where i=sqrt(-1) . It mov...
Text Solution
|
- If w=alpha+ibeta, where beta!=0 and z!=1 , satisfies the condition tha...
Text Solution
|
- If z and bar z represent adjacent vertices of a regular polygon of n s...
Text Solution
|
- I f|z|=max{|z-1|,|z+1|}, then
Text Solution
|
- If omega is a cube root of unity but not equal to 1, then minimum valu...
Text Solution
|
- The shaded region, where P = (-1,0) ,Q = (-1 + sqrt(2) , sqrt(2) )R =...
Text Solution
|