Topper's Solved these Questions
QUADRILATERALS
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revision Exercise (long Answer Questions)|5 VideosQUADRILATERALS
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revision Exercise (very Short Answer Questions)|10 VideosPROBABILITY
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revision Exercise (very Short Answer /short Answer Questions)|10 VideosSTATISTICS
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revision Exercise|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH-QUADRILATERALS-Revision Exercise (short Answer Questions )
- In an isosceles-trapezium, show that the opposite angles are supplemen...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure ABCD is a parallelogram. AB = (2x+25) cm, CD = (3x...
Text Solution
|
- ABCD is a parallelogram and AE and CF bisect angleA and angleC respect...
Text Solution
|
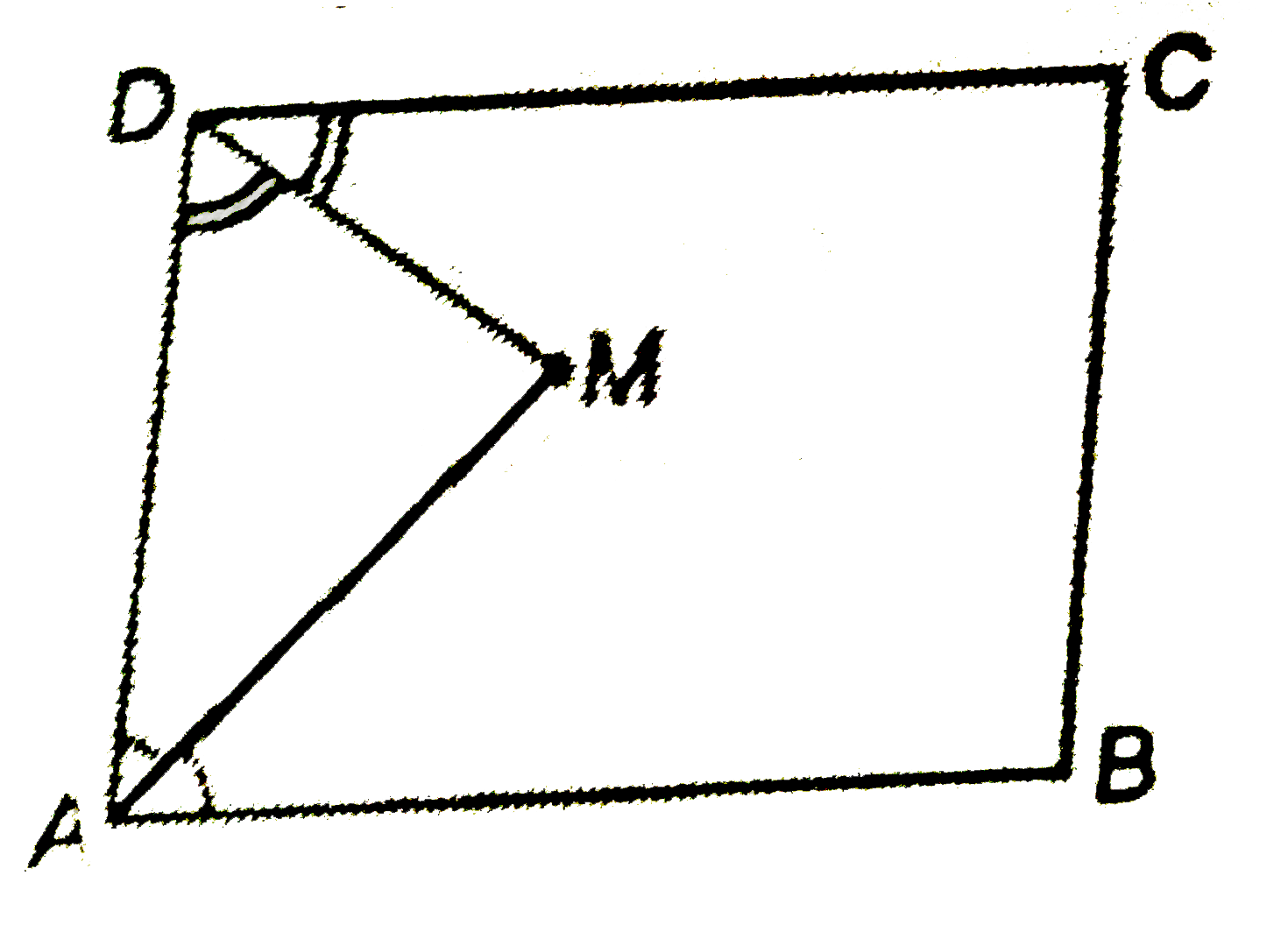
- In the given figure, AM bisects angle A and DM bisects angle D of para...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove that AB = 2BC.
Text Solution
|
- E and F are points on diagonal AC of a parallelogram ABCD such that AE...
Text Solution
|
- In a quadrilateral ABCD, AB= AD and CB= CD. Prove that: AC is perpe...
Text Solution
|
- In the adjoining figure, ABCD is a rhombus and ABE is an equilateral t...
Text Solution
|
- In a trapezium ABCD, if E and F be the mid-points of diagonal AC and B...
Text Solution
|
- In a quadrilateral ABCD the linesegment bisecting angleC and angleD me...
Text Solution
|