Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
PROBABILITY
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise MISCELLANEOUS EXERCISE|10 VideosPROBABILITY
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise MCQ_TYPE|20 VideosPRINCIPLE OF MATHEMATICAL INDUCTION
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 4.1|1 VideosRELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise MISCELLANEOUS EXERCISE|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH-PROBABILITY-NCERT QUESTIONS
- Three coins are tossed. Describe (i) Two events which are mutually exc...
Text Solution
|
- Two dice are thrown. The events A, B and C are as follows:A : getting...
Text Solution
|
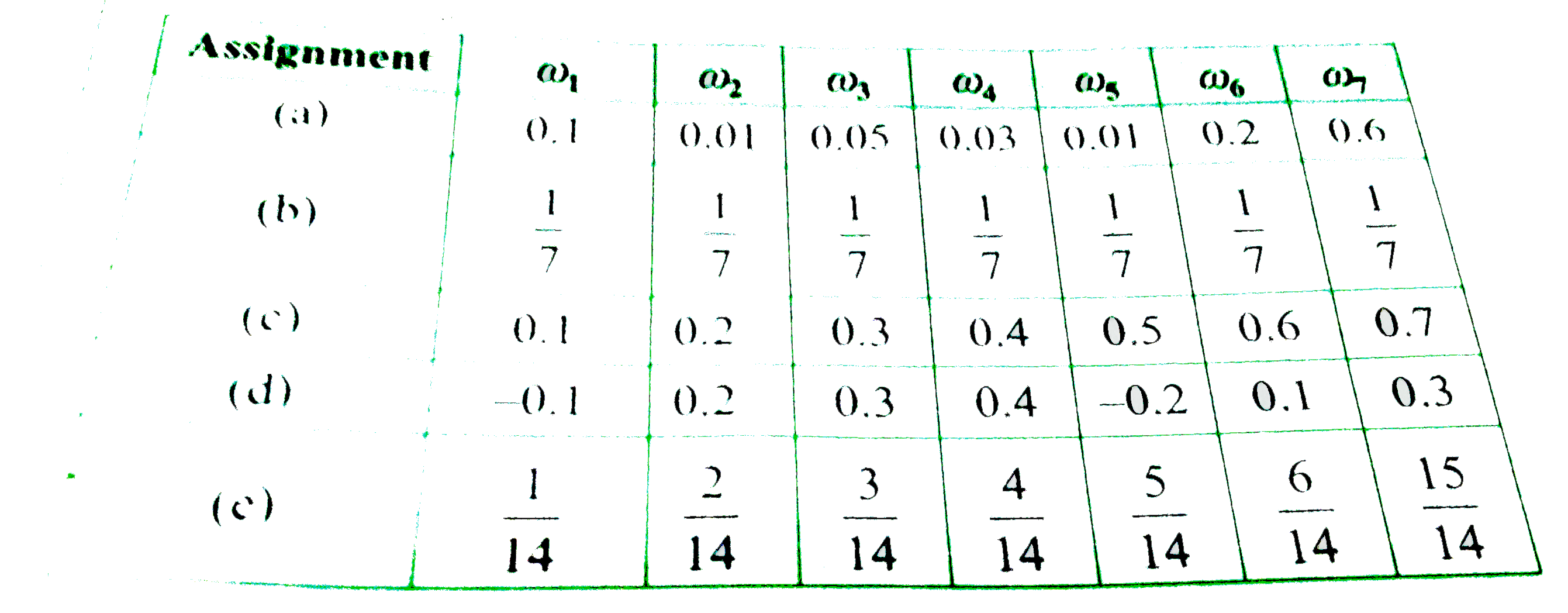
- Which of the following cannot be valid assignment of probabilities for...
Text Solution
|
- A coin a tossed twice, that is the probability that at least one tail...
Text Solution
|
- A die is thrown, find the probability of following events: (i) A ...
Text Solution
|
- A card is selected from a pack of 52 cards. (a) How many points are...
Text Solution
|
- A fair coin with 1 marked on one face and 6 on the other and a fair...
Text Solution
|
- There are four men and six women on the city council. If one counci...
Text Solution
|
- A fair coin is tossed four times, and people win Re 1 for each head...
Text Solution
|
- Three coins are tossed once. Fmd the probability of getting (i) 3 h...
Text Solution
|
- If 2/(11)is the probability of an event, what is the probability of t...
Text Solution
|
- A letter is chosen at random from the word ASSASSINATION. Find the ...
Text Solution
|
- In a lottery, a person choses six different natural numbers at rand...
Text Solution
|
- Check whether the following probabilities P(A) and P(B) are consistent...
Text Solution
|
- Fill in the blanks in following table:
Text Solution
|
- Give P(A) =3/5and P(B) =1/5dotFind P(A or B), if A and B are mutually ...
Text Solution
|
- If E and F are events such that P(E)=1/4, P(F)=1/2 and P(E"and"F)=1/8,...
Text Solution
|
- Events E and F are such that P(not E or not F) = 0. 25, State whether ...
Text Solution
|
- A and B are events such that P(A) = 0. 42, P(B) = 0. 48and P(A a n d B...
Text Solution
|
- In class XI of a school 40% of the students study Mathematics and 3...
Text Solution
|