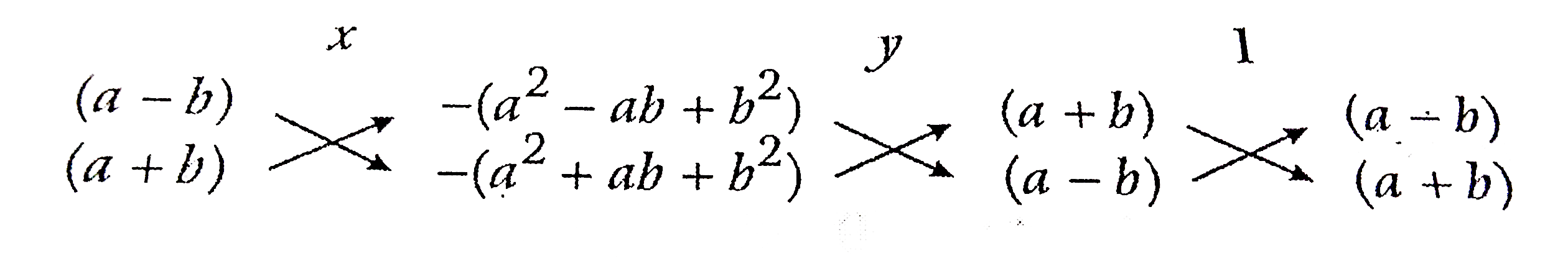Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3a|18 VideosLINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Exercise 3A|8 VideosINTRODUCTION TO TRIGONOMETRY
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revision Exercise Long Answer Questions|5 VideosPOLYNOMIALS
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH|Exercise Revision Exercise Long Answer Questions|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NAGEEN PRAKASHAN ENGLISH-LINEAR EQUATIONS IN TWO VARIABLES -Revision Exercise Long Answer Questions
- Solve : a(x+y)+b(x-y)=a^2-a b+b^2, a(x+y)-b(x-y)=a^2+a b-b^2
Text Solution
|
- Solve for x and y, px + qy = 1 and qx + py = ((p + q)^(2))/(p^2 + q^2...
Text Solution
|
- Solve (x + ab)/(2) = (y + ab)/(2) and ax + by = a^(2) + b^(2).
Text Solution
|
- Solve (x)/(a) + (y)/(b) = 1 and a(x - a)- b(y + b) = 2a^(2) + b^(2).
Text Solution
|
- Acid with 25% and 40% concentration are mixed to get 60 litres of 30% ...
Text Solution
|
- A trader purchases 4 bags of rice and 10 bags of wheat for Rs. 3600. H...
Text Solution
|
- A jeweller has bars of 18 carat gold and 12 carat gold. How much of ea...
Text Solution
|
- Divide c into two parts such that a times the larger part shall be equ...
Text Solution
|
- I bought 5 pens, 7 pencils and 4 erasers. Rajan bought 6 pens, 8 erase...
Text Solution
|