Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PSEB-MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLID-EXERCISE
- Figure 9.11 shows the strain-stress curve for a given material. What a...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 9.11 shows the strain-stress curve for a given material. What a...
Text Solution
|
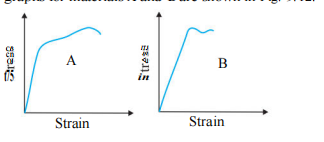
- The stress-strain graphs for materials A and B are shown in Fig. 9.12....
Text Solution
|
- The stress-strain graphs for materials A and B are shown in Fig. 9.12....
Text Solution
|
- Read the following two statements below carefully and state, with reas...
Text Solution
|
- Read the following two statements below carefully and state, with reas...
Text Solution
|
- Two wires of diameter 0.25 cm, one made of steel and the other made of...
Text Solution
|
- The edge of an aluminium cube is 10 cm long. One face of the cube isfi...
Text Solution
|
- Four identical hollow cylindrical columns of mild steel support a big ...
Text Solution
|
- A piece of copper having a rectangular cross-section of 15.2 mm xx 19....
Text Solution
|
- A steel cable with a radius of 1.5 cm supports a chairlift at a ski ar...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid bar of mass 15 kg is supported symmetrically by three wires ea...
Text Solution
|
- A 14.5 kg mass, fastened to the end of a steel wire of unstretched len...
Text Solution
|
- Compute the bulk modulus of water from the following data: Initial vol...
Text Solution
|
- What is the density of water at a depth where pressure is 80.0 atm, gi...
Text Solution
|
- Compute the fractional change in volume of a glassslab, when subjected...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the volume contraction of a solid copper cube, 10 cm on an e...
Text Solution
|
- How much should the pressure on a litre of water be changed to compres...
Text Solution
|
- Anvils made of single crystals of diamond, with the shape as shown in ...
Text Solution
|
- A rod of length 1.05 m having negligible mass is supported at its ends...
Text Solution
|