Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PSEB-THERMODYNAMICS-EXERCISE
- A geyser heats water flowing at the rate of 3.0 litres per minute from...
Text Solution
|
- What amount of heat must be supplied to 2.0 xx 10^-2 kg of nitrogen (a...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2 if brought ...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why The coolant in a chemical or a nuclear plant (i.e., the li...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why Air pressure in a car tyre increases during driving.
Text Solution
|
- Explain why The climate of a harbour town is more temperate than that ...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder with a movable piston contains3moles of hydrogen atstandard...
Text Solution
|
- In changing the state of a gas adiabatically from an equilibrium state...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other vi...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other vi...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other vi...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylinders A and B of equal capacity are connected to each other vi...
Text Solution
|
- A steam engine delivers 5.4 xx 10^8J of work per minute and services 3...
Text Solution
|
- An electric heater supplies heat to a system at a rate of 100W. If sys...
Text Solution
|
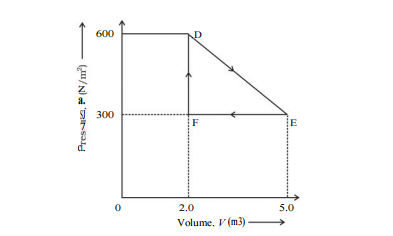
- A thermodynamic system is taken from an original state to an intermedi...
Text Solution
|
- A refrigerator isto maintain eatables kept inside at 9^@C. If room tem...
Text Solution
|