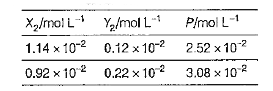A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- Consider the equilibrium X(2) + Y(2) hArr P. Find the stoichiometric c...
Text Solution
|
- If 'alpha' be the angle subtended by the points P(x(1),y(1)) and Q(x(2...
Text Solution
|
- If the normal at the point P(x(i),y(i)),i=1,2,3,4 on the hyperbola xy=...
Text Solution
|
- Theorem: The distance between two points P(x1;y1) and Q(x2;y2) is give...
Text Solution
|
- Property 4: The equation of the family of circles passing through two ...
Text Solution
|
- Normals at (x(1),y(1)),(x(2),y(2))and(x(3),y(3)) to the parabola y^(2)...
Text Solution
|
- बिंदु P(x(1), y(1)) और Q (x(2),y(2)) के बीच की दूरी ज्ञात करें।
Text Solution
|
- The coordinates of the midpoint joining P(x(1),y(1)) and Q(x(2),y(2)...
Text Solution
|
- If x(1), x(2), x(3) as well as y(1), y(2), y(3) are in G.P with same c...
Text Solution
|