Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
VERY SIMILAR TEST 5
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION B (ZOOLOGY) GROUP A|10 VideosVERY SIMILAR TEST 5
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION B (ZOOLOGY) GROUP B|9 VideosVERY SIMILAR TEST 5
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION A (BOTANY) GROUP B|9 VideosVERY SIMILAR TEST 4
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise SECTION B (ZOOLOGY) (GROUP C)|4 VideosVERY SIMILAR TEST 7
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN|Exercise Section B (ZOOLOGY) (Group C)|7 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
ARIHANT PRAKASHAN-VERY SIMILAR TEST 5-SECTION A (BOTANY) GROUP C
- Describe the structure of DNA?
Text Solution
|
- Answer any two of the following questions each within 200 words: Des...
Text Solution
|
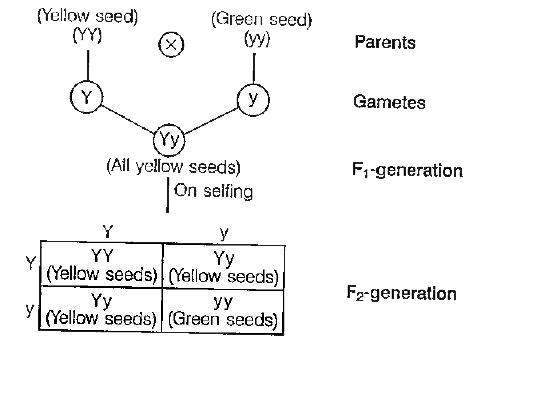
- Explain monohybrid cross taking seed coat colour as a trait in Pisum s...
Text Solution
|
- Answer any two of the following questions each within 200 words: Bri...
Text Solution
|