Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
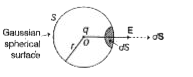
- Deduce Coulomb.s law from Gauss. law of electrostatics.
Text Solution
|
- State Gauss's Theorem in electrostatics and deduce coulomb's law from ...
Text Solution
|
- स्थिर वैधुत में गाउस के नियम को बताइये। इसकी सहायता से कुल|म के नियम (...
Text Solution
|
- Deduce coulomb's law in electrostatics from Gauss theorem. Or State an...
Text Solution
|
- State and explain Gauss's theorem in Electrostatics.
Text Solution
|
- State and explain Gauss's theorem in Electrostatics.
Text Solution
|
- State Gauss' law in electrostatic.
Text Solution
|
- State Coulomb.s law
Text Solution
|
- State and prove Gauss' law in electrostatics. Define.
Text Solution
|