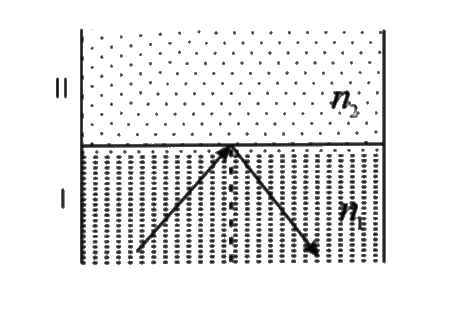
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A light ray moving in medium-I (of refractive index n(1)) is incident ...
Text Solution
|
- In the diagram shown, light is incident on the interface between media...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light travels from a medium of refractive index n(1) to a m...
Text Solution
|
- प्रकाश की एक किरण n(1) अपवर्तनांक के एक माध्यम से n(2) अपवर्तनांक के द...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on a medium at an angle i. It is found tha...
Text Solution
|
- A light ray moving in medium-I (of refractive index n(1) ) is incident...
Text Solution
|
- एक प्रकाश किरण माध्यम (1) से माध्यम (2) में अपवर्तित होती है| इनके अपव...
Text Solution
|
- The critical angle of a medium-air interface is 30^(@) . The refracti...
Text Solution
|
- Light ray is travelling from a medium of refractive index mu in to air...
Text Solution
|