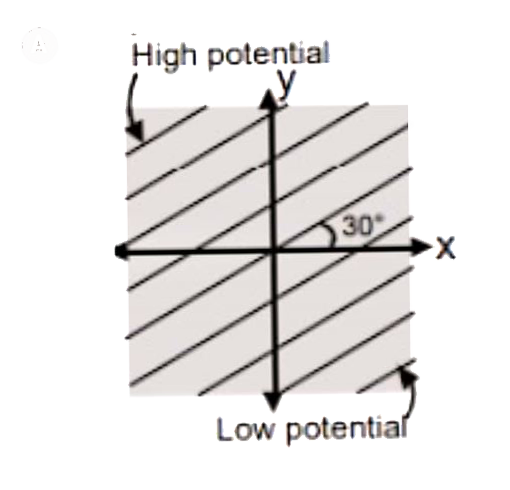
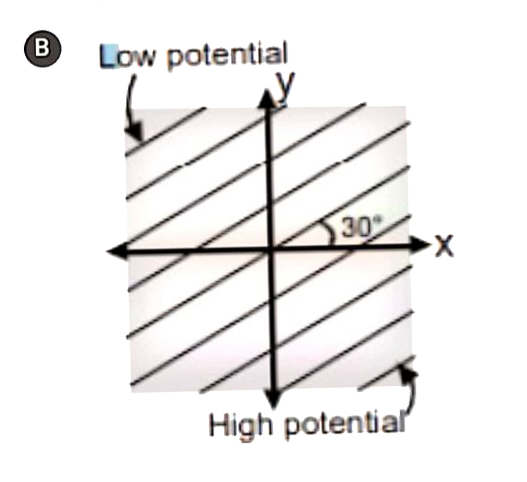
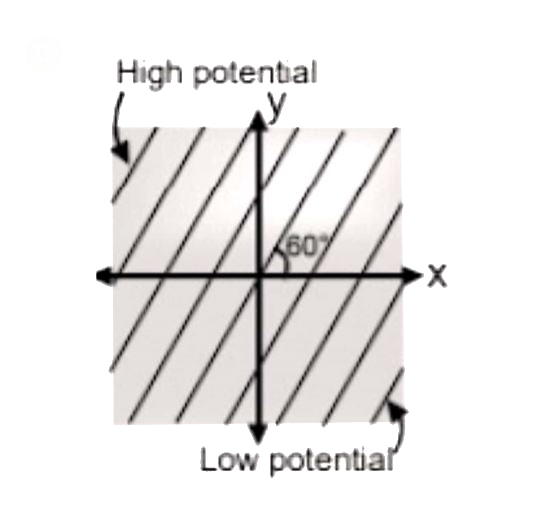
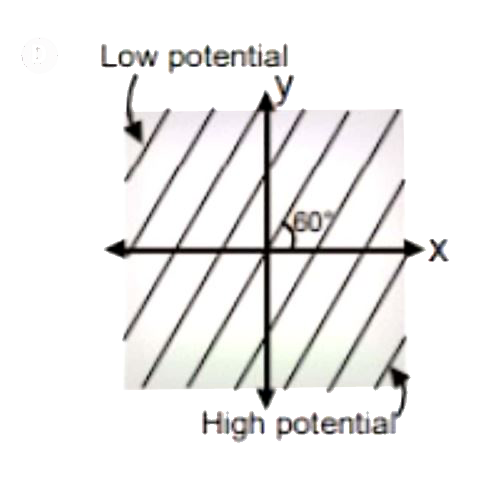
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The electric field intensity at all points in space is given by vecE =...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field intensity at all points in space is given by vecE =...
Text Solution
|
- The electirc potential at a point (x, y, z) is given by V = -x^(2)y ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the potential phi of an electric field given by vecE=a(y hati+x h...
Text Solution
|
- किसी समविभावी पृष्ठ (equipotential surface ) S के एक बिन्दु P पर विधुत...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field intensity in a region is given by vecE=(-xhati+yhat...
Text Solution
|
- The electric potential V at any point (x, y, z) in space is given by V...
Text Solution
|
- The electric field is given by vecE=(A)/(x^(3))hati+By hatj+Cz^(2)hatk...
Text Solution
|
- x - y तल में किसी बिन्दु (x,y) पर विद्युतीय विभव V = -kxy द्वारा दिया ...
Text Solution
|