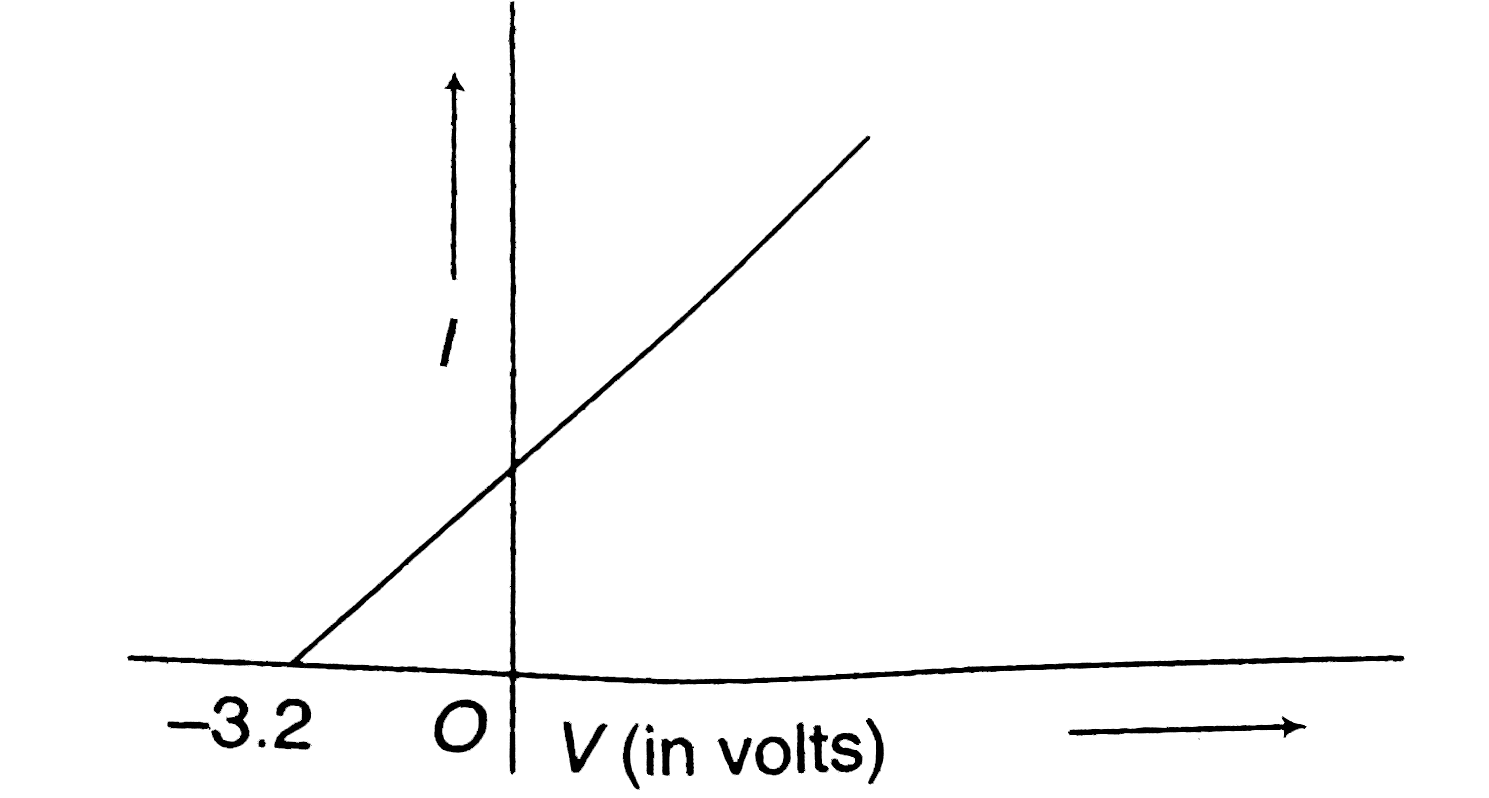
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In a photoelectric experiment the relation between applied potential d...
Text Solution
|
- In an experiment on photoelectic effect, the graph as shown in fig. we...
Text Solution
|
- At frequencies of the incident radiation above the threshold frequency...
Text Solution
|
- In photoelectric experiment the plot between anode potential and photo...
Text Solution
|
- In a photoelectric experiment, the graph of frequency v of incident li...
Text Solution
|
- The threshold frequency of the metal of the cathode in a photoelectric...
Text Solution
|
- In a photoelectric experiment the relation between applied potential d...
Text Solution
|
- In a photoelectric experiment, the reciprocal of the slope of the st...
Text Solution
|
- Draw a graph showing variation of photoelectric current (I) with anode...
Text Solution
|