A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A hemispherical cavity of radius R is created in a solid sphere of rad...
Text Solution
|
- The figure represents a solid uniform sphere of mass M and radius R. A...
Text Solution
|
- A cavity of radius r is made inside a solid sphere. The volume charge ...
Text Solution
|
- There is a concentric hole of radius R in a solid sphere of radius 2R....
Text Solution
|
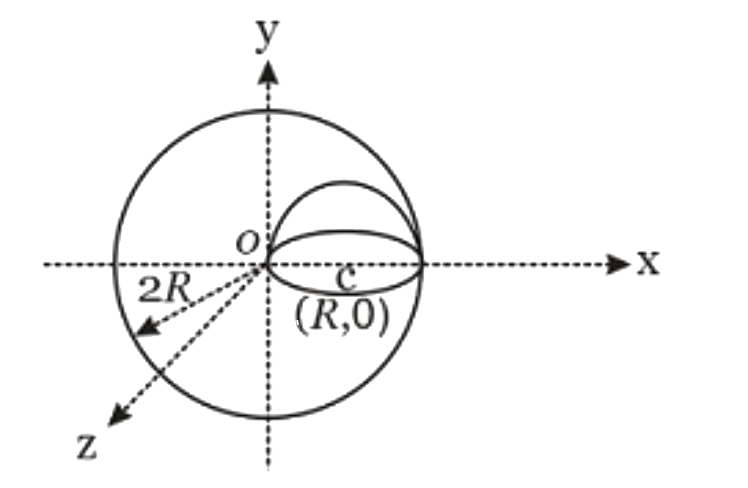
- A hemi-spherical cavity is created in solid sphere (of radius 2R ) as ...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical cavity is formed a solid sphere by removing mass from it....
Text Solution
|
- A cavity of radius r is made inside a solid sphere. The volume charge ...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of radius R has a spherical cavity of radius r as shown...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a solid sphere of density rho and radius 4R . Centre of the s...
Text Solution
|