A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
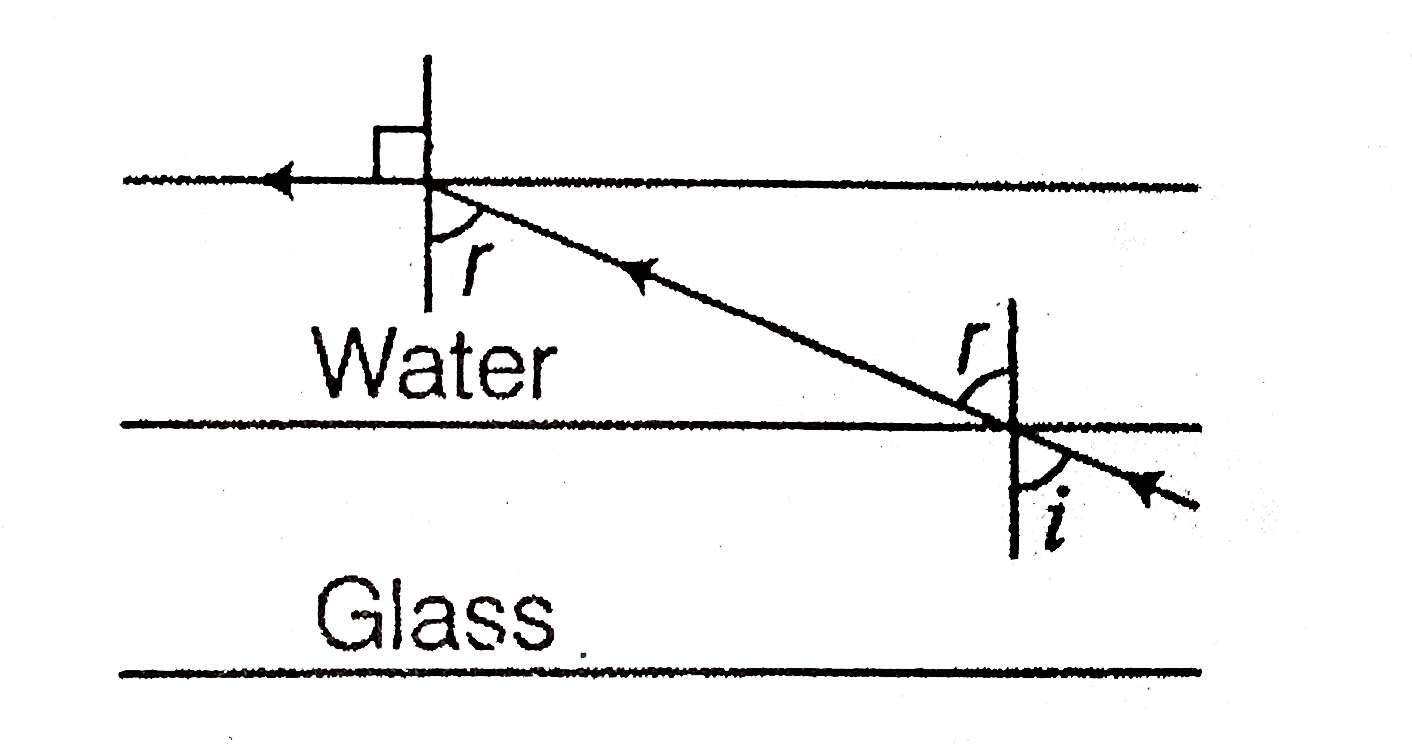
- A ray of light is incident at the glass-water interface at an angle i ...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident at the glass-water interface at an angle I,...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident at the glass-water interface at an angle i....
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a glass (mu(g) = 1.5) vessel, partly filled with water (...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light passes from glass (mu(g) = 1.52) to water (mu(w) = 1.33...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident on the interface between water and glass at...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident at the glass-water interface at an angle i ...
Text Solution
|
- एक प्रकाश - किरण काँच - जल अंतरापृष्ठ पर कोण I पर आपतित होती है तथा अं...
Text Solution
|
- A ray of light is incident at the glass-water interface at an angle i,...
Text Solution
|