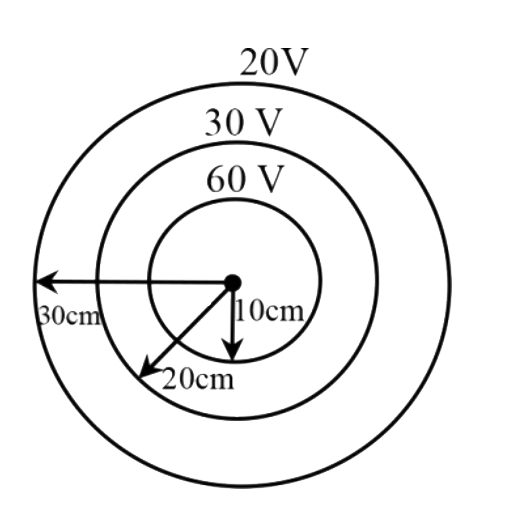
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A few spherical equipotential surfaces are shown in the figure. The el...
Text Solution
|
- Some equipotential surfaces are shown in figure . The magnitude and ...
Text Solution
|
- A family of equipotential surface are shown. The direction of the elec...
Text Solution
|
- The angle between the equipotential surface and the electric field (or...
Text Solution
|
- Some equipotential surface are shown in the figure. Find the value of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two spherical shells are as shown in figure. Suppose r is the distance...
Text Solution
|
- A few spherical equipotential surfaces are shown in the figure. The el...
Text Solution
|
- For a spherical capacitor shown at which points the electric field wil...
Text Solution
|
- Equipotential surface through a point is………… to the electric field at ...
Text Solution
|